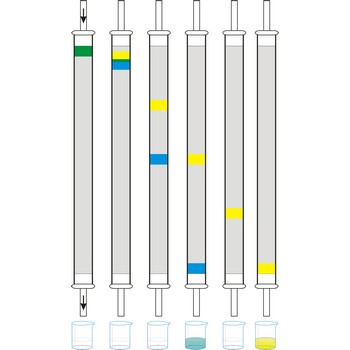
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
dysprosium → disprozij
Dysprosium was discovered by Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran (France) in 1886. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word dysprositos meaning hard to obtain. It is soft, lustrous, silvery metal. Reacts with oxygen. Reacts rapidly with water; dissolves in acids. Metal ignites and burns readily. Reductant. Dysprosium usually found with erbium, holmium and other rare earths in some minerals such as monazite sand. Dysprosium uses are limited to the experimental and esoteric. Some isotopes of dysprosium are effective absorbers of thermal neutrons and are being considered for use in the control rods in nuclear reactors.
Einstein equation → Einsteinova jednadžba
Einstein equation is the mass-energy relationship introduced by Albert Einstein in 1905 in the form E = mc2, where E is a quantity of energy, m its mass, and c is the speed of light. It presents the concept that energy possesses mass.
rate equation → jednadžba brzine reakcije
Rate equation is an equation that describes the dependence of reaction rate on concentrations of reacting species. It always has the form
where a and b are usually integral exponents.
thermionic emission → termionska emisija
Thermionic emission is the boiling off of electrons from heated metals. It gives a source of electrons for cathode ray tubes.
unit cell → jedinična ćelija
Unit cell is the smallest fragment of the structure of a solid that by repetition can generate the entire structure.
viscosity → viskozitet
Viscosity. (η) (coefficient of viscosity) is the resistance a liquid exhibits to flow. Experimentally, the frictional force between two liquid layers moving past each other is proportional to the area of the layers and the difference in flow speed between them.
electron → elektron
The electron is an elementary particle with a negative electric charge of (1.602 189 2±0.000 004 6)×10-19 C and a mass of 1/1837 that of a proton, equivalent to (9.109 534±0.000 047)×10-31 kg.
In 1897 the British physicist Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson (1856-1940) discovered the electron in a series of experiments designed to study the nature of electric discharge in a high-vacuum cathode-ray tube. Thomson interpreted the deflection of the rays by electrically charged plates and magnets as evidence of bodies much smaller than atoms that he calculated as having a very large value for the charge to mass ratio. Later he estimated the value of the charge itself.
Electrons are arranged in from one to seven shells around the nucleus; the maximum number of electrons in each shell is strictly limited by the laws of physics (2n2). The outer shells are not always filled: sodium has two electrons in the first shell (2×12 = 2), eight in the second (2×22 = 8), and only one in the third (2×32 = 18). A single electron in the outer shell may be attracted into an incomplete shell of another element, leaving the original atom with a net positive charge. Valence electrons are those that can be captured by or shared with another atom.
Electrons can be removed from the atoms by heat, light, electric energy, or bombardment with high-energy particles. Decaying radioactive nuclei spontaneously emit free electrons, called β particles.
energy → energija
Energy (E, U) is the characteristic of a system that enables it to do work. Like work itself, it is measured in joules (J).
The internal energy of a body is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy of its component atoms and molecules.
Potential energy is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy).
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is usually defined as the work that will be done by a body possessing the energy when it is brought to rest. For a body of mass m having a speed v, the kinetic energy is mv2/2. Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
In an isolated system energy can be transferred from one form to another but the total energy of the system remains constant.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Wagnerova cijev." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table