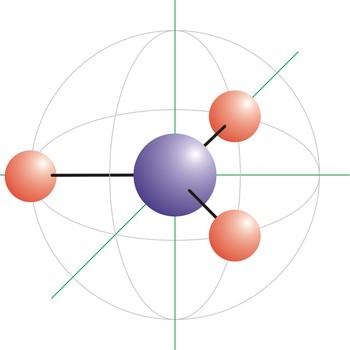
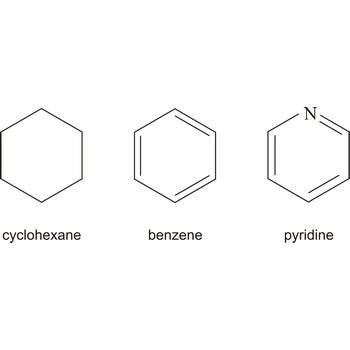
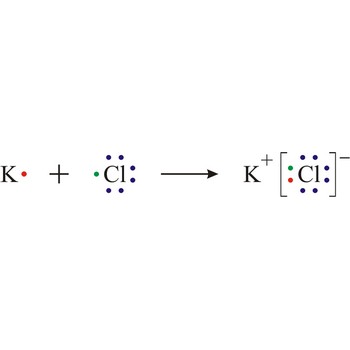Lewis structure → Lewisova struktura
Lewis structure is the representation of the electron arrangement in atoms, ions, or molecules by showing the valence electrons as dots placed around the symbols for the elements.
Lewis acid → Lewisova kiselina
Lewis acid is an agent capable of accepting a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Lewis base → Lewisova baza
Lewis base is an agent capable of donating a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Lewis number → Lewisova značajka
Lewis number (Le) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where a is thermal diffusivity and D is diffusion coefficient.
primary structure of proteins → primarna struktura proteina
Primary structure of proteins is a sequence of defined amino acids in some protein.
planary structure → planarna struktura molekule
Planary structure of molecule is a structure of molecule in which all atoms in the molecule lie in the same plane.
ringlike structure → prstenasta struktura
The ringlike structure is a structure by which the cycloalcanes and aromates are shown.
condensed structural formulas → kondenzirane strukturne formule
Condensed structural formulas are shortened and easier layout of structural formulas of organic compounds (butane, CH3(CH2)2CH3).
structural isomer → strukturni izomer
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same formula, but different constituents. Dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH), for example, are constitutional isomers with general formula C3H6O.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Lewisova struktura." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table