catalytic cracking → katalitčko krekiranje
Catalytic cracking is a petroleum refining process in which heavy-molecular weight hydrocarbons are broken up into light hydrocarbon molecules by the application of heat and pressure in the presence of a catalyst.
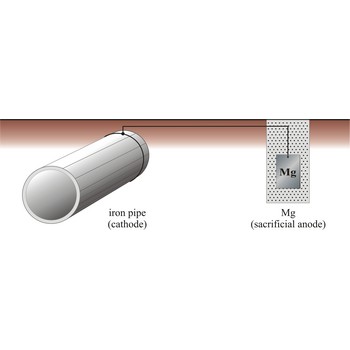
cathodic protection → katodna zaštita
Cathodic protection is a process in which a structural metal, such as iron, is protected from corrosion by connecting it to a metal that has a more negative reduction half-cell potential, which now corrodes instead of iron. There are two major variations of the cathodic method of corrosion protection. The first is called the impressed current method, and the other is called the sacrificial anode method.
chain reaction → lančana reakcija
Chain reaction is a reaction done in three steps: initiation in which usually radicals are made which react with other molecules in stage of propagation and, when all reactants are spent, it ends by termination when all available radicals are completely spent.
Nuclear chain reaction refers to a process in which neutrons released in fission produce an additional fission in at least one further nucleus. Nuclear power plants operate by precisely controlling the rate at which nuclear reactions occur. On the other hand, nuclear weapons are specifically engineered to produce a reaction that is so fast and intense it cannot be controlled after it has started.
detection limits → granica detekcije
Detection limits is the smallest quantity of analyte which it is possible to determine by means of a given technique or procedure.
dynamic equilibrium → dinamička ravnoteža
Dynamic equilibrium is established when two opposing processes are occurring at precisely the same rate, so that there is no apparent change in the system over long periods of time.
elution → eluacija
Elution is the process of removing an adsorbed material (adsorbate) from an adsorbent with a liquid (eluent). The solution consisting of the adsorbate dissolved in the eluent is the eluate. Elution is the process used to wash components of a mixture through a chromatography column.
flotation → flotacija
Flotation is a procedure in which hydrophobic solid substances are separated from hydrophilic one using bubbles of air. If air is blow through a suspension, in which substances promoting easier creation of foam are added, bubbles of air are created which stick to the hydrophobic matter and carry it out to the surface.
chemical change → kemijska promjena
Chemical change is a process which results in the production of one or more new materials. The system within which the process takes place is called a chemical system. A chemical change is also known as a chemical reaction, where one substance is converted into one or more different substances. When sodium and chlorine react to produce sodium chloride, a chemical reaction has taken place.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Carnotov kružni proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table