chemical engineering → kemijsko inženjerstvo
Chemical engineering is the branch of engineering that is concerned with the design, construction and operation of the plants and machinery used in industrial chemical processes.
coagulation → koaguliranje
Coagulation is a process of colloid particles merging into bigger ones. By removing the charge form a colloid ion, by increasing the temperature or by increasing electrolyte concentration, colloid particles will gather into bigger groups precipitate will emerge. Precipitate that is formed in this way (coagulate) is amorphic and considerably polluted with adsorbed pollutants.
coal → ugljen
Coal is a black or brownish-black, combustible sedimentary rock, with 30 % (lignite) to 98 % (anthracite) carbon by weight, mixed with various amounts of water and small amounts of sulfur and nitrogen compounds. It is formed from plant matter that decayed in swamps and bogs that has been compressed and altered by geological processes over millions of years. Coal is primarily used as a fuel.
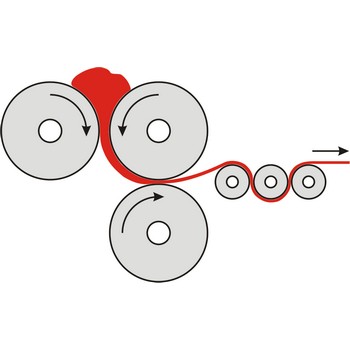
calendering → kalandriranje
Calendering is the process of forming materials to make a film/sheet by passing them through a series of hot rollers.
carbon → ugljik
Carbon has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word carbo meaning charcoal. Graphite form of carbon is a black, odourless, slippery solid. Graphite sublimes at 3825 °C. Diamond form is a clear or colored; an extremely hard solid. C60 is Buckminsterfullerine. Carbon black burns readily with oxidants. Carbon is made by burning organic compounds with insufficient oxygen. There are close to ten million known carbon compounds, many thousands of which are vital to organic and life processes. Radiocarbon dating uses the carbon-14 isotope to date old objects.
catalyst → katalizator
Catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. Catalysts that have the same phase as the reactants are homogenous catalysts (e.g. enzymes in biochemical reactions). Those that have a different phase are heterogeneous catalyst (e.g. metals or oxides used in gas reactions).
The catalyst provides an alternative pathway by which the reaction can proceed, in which the activation energy is lower. In thus increases the rate at which the reaction comes to an equilibrium, although it does not alter the position of the equilibrium.
computational chemistry → kompjutacijska kemija
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry concerned with the prediction or simulation of chemical properties, structures, or processes using numerical techniques.
concentration of ore → koncentriranje ruda
Concentration of ores is important industrial processes and is the first steps to the extraction of the metals. Normally, the ore is concentrated by separating it from the clay body in which it occurs either by gravity, sedimentation, or by a floatation process, before the extraction of the metal from the ore is started.
conduction → kondukcija
This process occurs most significantly in solids. The atoms or molecules in a solid state do not leave their mean positions, but continue to vibrate about their mean positions. They transfer heat energy from one atom to another. This happens because of the coupling between them due to mutually attractive forces.
crystallisation → kristalizacija
Crystallisation is process in which the melted substance from a saturated solution turns into solid substance (crystal).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Carnotov kružni proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table