overpotential → prenapon
Overpotential (η) is a potential that must be applied in an electrolytic cell in addition to the theoretical potential required to liberate a given substance at an electrode. The value depends on the electrode material and on the current density.
positive pole → pozitivni pol
Positive pole is that half-cell in the electrochemical cell which has the most positive electrode potential.
reaction layer → reakcijski sloj
Reaction layer (in electrochemistry) is that layer of solution adjacent to an electrode within which a stationary distribution of electroactive species is established as the result of homogeneous reaction.
reversible cell → povrativi članak
Reversible cell is an electrical cell the chemical action in which can be reversed by passing through it a current opposite in direction to that generated by the cell.
voltametry → voltametrija
Voltametry is a common name for a large group of instrumental techniques which are based on measuring the electric current formed by a continuous potential shifting on the electrodes.
electrogravimetry → electrogravimetrija
Electrogravimetry is an electroanalytical technique in which the substance to be determined (usually a metal) is deposited out on an electrode which is weighed before and after the experiment. The potential of the electrode must be carefully chosen to ensure that only the metal do be determined will deposit.
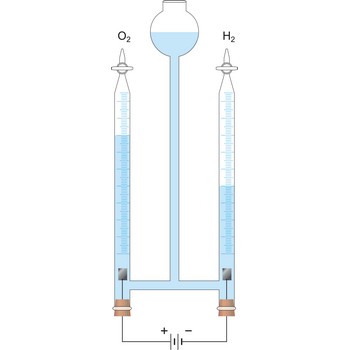
electrolysis → elektroliza
Electrolysis is the decomposition of a substance as a result of passing an electric current between two electrodes immersed in the sample.
electrophoresis → elektroforeza
Electrophoresis is a technique for the analysis and separation of colloids, based on the movement of charged colloidal particles in an electric field. The migration is toward electrodes of charge opposite to that of the particles. The rate of migration of the particles depends on the field, the charge on the particles, and on other factors, such as the size and shape of the particles.
Electrophoresis is important in the study of proteins. The acidity of the solution can be used to control the direction in which a protein moves upon electrophoresis.
electroplating → galvaniziranje
Electroplating (also called electrodeposition) is the deposition of a metallic coating onto an object by putting a negative charge onto the object and immersing it into a solution which contains a salt of the metal to be deposited. The metallic ions of the salt carry a positive charge and are attracted to the part. When they reach it, the negatively charged part provides the electrons to reduce the positively charged ions to metallic form.
Typically, a brass or nickel object is coated with a layer of silver by making use of electrolysis of a silver solution, using the object to be coated as the cathode. The anode consist of pure silver, and the cathode is the object to be plated. The electrolyte is a mixure of silver nitrate with potassium cyanide. The reactions are:
The cyanide ensures a low concentration of silver ions, a condition for providing the best plating results.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "CO2 ion selektivna elektroda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table