aspartic acid → asparaginska kiselina
Aspartic acid is an electrically charged amino acids with acidic side chains. As a group the charged amino acids are relatively abundant and are generally located on the surface of the protein. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Aspartic acid (sometimes referred to as asparate depending on pH) is non-essential in mammals, being produced from oxaloacetate by transamination.
- Abbreviations: Asp, D
- IUPAC name: 2-aminobutanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H7NO4
- Molecular weight: 133.10 g/mol
buffer capacity → puferski kapacitet
Buffer capacity is number of moles of a strong acid or a strong base needed to change pH of 1 dm3 of buffer solution for pH unit.
californium → kalifornij
Californium was discovered by Stanley G. Thompson, Kenneth Street Jr. and Albert Ghiorso (USA) in 1950. Named after the State and University of California, USA. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Powerful neutron emitter. Californium was made by bombarding curium with helium ions.
atmosphere → atmosfera
1. Atmosphere is the column of air which is extending several hundred kilometers above the surface the Earth's surface. The density of this air decreases as you proceed up from the surface. The air in the atmosphere consists of 78 % nitrogen, 21 % oxygen, and 0.9 % argon. The remaining 0.1 % of the atmosphere consists of ozone, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, helium, and neon. The atmosphere is divided into different regions. The lowest two layers are the troposphere (the layer closest to the earth) and the stratosphere respectively. These two layers contain more than 99 % of the atmospheric molecules.
2. Standard atmosphere (atm) is an obsolete pressure and stress unit which should be discontinued. It is unit of pressure equal to the air pressure measured at mean sea level.
1 atm = 101 325 Pa
Technical atmosphere (at) is an obsolete MKpS pressure and sttress derived unit.
1 at = 98 066.5 Pa
1 atm = 1.033 227 453 at
autocatalysis → autokataliza
Autocatalysis is a reaction in which its product can act as a catalyst. Oxalate oxidation with permanganate in an acid solution is a slow reaction
Mn2+-ions catalyse this reaction. When enough Mn2+-ions are created, the reaction occurs instantly.
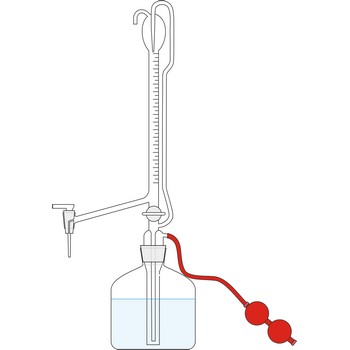
automatic burette → automatska bireta
Automatic burette is used for series of tests. It is connected with a bottle which contains the titration solution. The air is pumped into the bottle by a small rubber air pump, created the pressure in the bottle which the rises the solution to the top of burette. When the the burette is full, the valve is released, the pressure in the bottle falls and the burette automatically sets itself to zero. Work with automatic burettes is by far faster and the consumption of standard solution is smaller.
calorimetry → kalorimetrija
Calorimetry is a measurement of the amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction, change of state, or formation of a solution, or any other event that includes heat transfer.
cation exchange → kationski izmjenjivač
Cation exchange is a cationic resin has positive ions built into its structure and therefore exchanges negative ions. In the cation exchange, the side groups are ionised acidic groups, such as (-SO3H, -COOH, -OH) to which cations H+ are attached. The exchange reaction is one in which different cations in the solution displace the H+ from the solid.
cementation → cementacija
Cementation is any metallurgical process in which the surfaces of a metal is impregnated by some other substance, especially an obsolete process for making steel by heating bars of wrought iron to red heat for several days in a bed of charcoal.
colligative properties → koligativna svojstva
Colligative properties are properties which affect a solvent based on the number of molecules of solute present such as melting point, boiling point and osmotic pressure.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vodena otopina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table