argon → argon
Argon was discovered by Lord Raleigh and Sir William Ramsay (Scotland) in 1894. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word argos meaning inactive. It is colourless and odourless noble gas. Chemically inert. It is the third most abundant element in the earth’s atmosphere and makes up about 1 %. Argon is continuously released into the air by decay of radioactive potassium-40. Pure form is obtained from fractional distillation of liquid air. Used in lighting products. It is often used in filling incandescent light bulbs. Some is mixed with krypton in fluorescent lamps. Crystals in the semiconductor industry are grown in argon atmospheres.
Arrhenius equation → Arheniusova jednadžba
In 1889, Svante Arrhenius explained the variation of rate constants with temperature for several elementary reactions using the relationship
where the rate constant k is the total frequency of collisions between reaction molecules A times the fraction of collisions exp(-Ea/RT) that have an energy that exceeds a threshold activation energy Ea at a temperature of T (in kelvin). R is the universal gas constant.
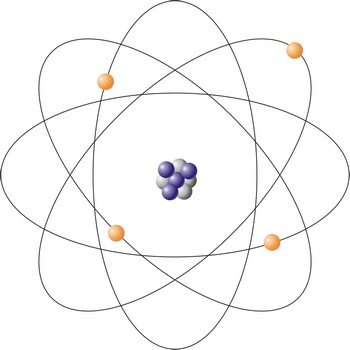
atom → atom
Atom is an atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element. Rutherford-Bohr’s model represents the atom as a positively charged core of a size around 10-14 m composed of protons (positive particles) and neutrons (neutral particles) around which negatively charged electrons circle. The number of protons and electrons are equal, so the atom is an electrically a neutral particle. Diameter of the atom is about 10-10 m.
Biot-Savart law → Biot-Savartov zakon
The magnetic field B due to a current-carrying conductor can be determined by Biot-Savart law. The contribution to magnetic field set up at distance r by the current element IdL is given by expression:
where μ0 is permeability constant. It plays a role in magnetic problems equivalent to the role of permittivity constant μ0 in electrostatics problems. In order to obtain B, contributions of all current elements have to be integrated. In case of a long straight conductor, carrying current I, Biot-Savart law gives:
SI unit for magnetic field B is tesla (T).
Permaeability constant μ0 has value 4π×10-7 T m A-1.
Bohr magneton → Bohrov magneton
Bohr magneton (μB) is the atomic unit of magnetic moment, defined as
where h is Planck’s constant, me the electron mass, and e the elementary charge. It is the moment associated with a single electron spin.
Born-Haber cycle → Born-Haberov kružni proces
Born-Haber cycle is a cycle of reactions used for calculating the lattice energies of ionic crystalline solids. For a compound MX, the lattice energy is the enthalpy of the reaction
The standard enthalpy of formation of the ionic solid is the enthalpy of the reaction
The cycle involves equating this enthalpy (which can be measured) to the sum of the enthalpies of a number of steps proceeding from the elements to the ionic solid. The steps are:
1) Atomization of the metal
2) Atomization of the nonmetal
3) Ionisation of the metal
This is obtained from the ionisation potential.
4) Ionisation of the nonmetal
This is electron affinity.
5) Formation of the ionic solids
Equation of the enthalpies gives
from which ΔHL can be found.
boron → bor
Boron compounds have been known for thousands of years, but the element was not discovered until 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy (England) and independently by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac (France) and L. J. Thenard (France). The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word buraq and the Persian word burah meaning boraks. It is hard, brittle, lustrous black semimetal. Unreactive with oxygen, water, alkalis or acids. Combines with most metals to form borides. Boron is obtained from kernite, a kind of borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O). High purity boron is produced by electrolysis of molten potassium fluroborate and potassium chloride (KCl). Amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares to provide a distinctive green color and in rockets as an igniter.
Faraday constant → Faradayeva konstanta
Faraday constant (F) is the electric charge of 1 mol of singly charged positive ions.
where NA is Avogadro’s constant (6.022×1023 mol-1) and e is the elementary charge (1.602×10-19 C).
brass → mjed
Brasses are alloys of copper and zinc (generally 5 % to 40 %). Brass has been known to man since prehistoric times, long before zinc itself was discovered. It was produced by melting copper together with calamine, a zinc ore. Its ductility reaches a maximum with about 30 % zinc and its tensile strength with 45 % although this property varies greatly with the mechanical and heat treatment of the alloy. Typical applications included gears, plumbing ware fittings, adapters, valves and screw machine products. The French horn is a valved brass wind instrument.
Brass may contain small amounts of other alloying elements, such as aluminum, lead, tin, or nickel. Lead can be added as an alloying element resulting in a brass that can be rapidly machined and produces minimal tool wear. Additions of aluminium, iron and manganese to brass improve strength, whilst silicon additions improve wear resistance. Brass containing tin (< 2 % ) is less liable to corrosion in seawater; it is sometimes called naval brass and is used in naval construction.

Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vi element." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table