periodic table of the elements → periodni sustav elemenata
Periodic table is a table of elements, written in sequence in the order of atomic number or atomic weight and arranged in horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups) to illustrate the occurrence of similarities in the properties of the elements as a periodic function of the sequence. The original form was proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, using relative atomic masses.
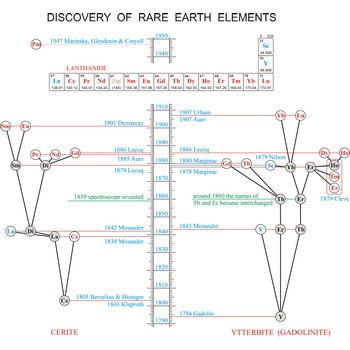
rare earth elements → elementi rijetkih zemalja
Rare earth elements (metals) are the elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), and the lanthanides (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu). These elements got their name from the fact that chemists first isolated them in their oxide forms. These oxides somewhat resemble calcium, magnesium and aluminium oxides, sometimes called common earths. Do you want to know more?
absorbed dose → apsorbirana doza
For any ionising radiation, absorbed dose (D) is the mean energy imparted to an element of irradiated matter divided by the mass of that element.
abundance of substances → rasprostranjenost tvari
Abundance of substances is the ratio of the total mass of a specified element in the Earth’s crust to the total mass of the Earth’s crust. It is often expressed as a percentage.
actinides → aktinoidi
Actinides (actinons or actinoids) are the fourteen elements from thorium to lawrencium inclusive, which follow actinium in the periodic table. The position of actinium is somewhat equivocal and, although not itself an actinide, it is often included with them for comparative purpose. The series includes the following elements: thorium (Th), protactinium (Pa), uranium (U), neptunium (Np), plutonium (Pu), amercium (Am), curium (Cm), berkelium (Bk), californium (Cf), einsteinium (Es), fermium (Fm), mendelevium (Md), nobelium (No) and lawrencium (Lr). Every known isotope of the actinide elements is radioactive. Traces of Pa, Np and Pu are consequently found, but only Th and U occur naturally to any useful extent.
alkali metal → alkalijski metal
Alkali metal is a term that refers to six elements: lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). These elements make up group 1 of the periodic table of elements. They all form singly charged positive ions, and are extremely reactive. They react violently with water, forming hydroxides and releasing hydrogen gas and heat. Caesium and francium are the most reactive and lithium is the least.
antiparticle → antičestica
Antiparticle is a particle having the same mass as a given elementary particle and a charge equal in magnitude but opposite in sign.
atomic number → atomski broj
Atomic number (Z) is a characteristic property of an element, equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number and the element symbol are two alternate ways to label an element. In nuclide symbols, the atomic number is a leading subscript; for example, in 2He.
Avogadro constant → Avogadrova konstanta
Avogadro constant (NA or L) is the number of elementary entities in one mole of a substance.
It has the value (6.022 045±0.000 031)×1023 mol-1.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vi element." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table