D-lines → D-linije
D-lines are two close lines in the yellow region of the spectrum of sodium, having wavelengths 589.6 nm (D1) and 589.0 nm (D2). They were labeled as feature D in the solar spectrum by German optician Joseph von Fraunhofer (1787-1826). As they a prominent and easily recognized they are used as a standard in spectroscopy.
diffraction grating → difrakcijska rešetka
Diffraction grating is a series of slits used to separate an incident wave into its component wavelengths by directionally separating their diffraction maxima.
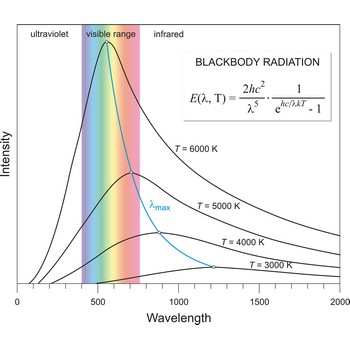
blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
geometrical optics → geometrijska optika
In most cases light can be described as an electromagnetic wave. Geometrical optics is an approximation in which the waves can be represented as straight-line rays. This approximation is valid if the light waves do not meet obstacles comparable in size to the wavelength of radiation.
light scattering → raspršenje
Light scattering is a type of diffuse reflection. When light strikes a rough surface, small flat areas are almost comparable to the wavelength, so the light scatters.
line spectrum → linijski spektar
Red-hot gases give line spectrum, i.e. is they emit electromagnetic rays of defined wavelengths. That kind of emission line of spectrum is characteristic of each chemical element.
microwave radiation → mikrovalna radijacija
Microwave radiation is a electromagnetic radiation with wavelength between 3 mm and 30 cm.
monochromator → monokromator
Monochromator (from the Greek words mono and chroma meaning single and colour) is an optical device based on dispersion of light by one or more prisms or diffraction gratings into its constituent wavelengths, which are utilized in turn.diffraction → difrakcija
Diffraction is the ability of a wave to bend around the edges of obstacles or holes. The effect is most noticeable when the obstacle or hole is comparable to the size of the wavelength
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Valno-čestična dualnost." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table