distilled water → destilirana voda
Distilled water is water purified by distillation so as to free it from dissolved salts and other compounds. Distilled water in equilibrium with the carbon dioxide in the air has conductivity of about 0.8×10-6 S cm-1. Repeated distillation in vacuum can bring conductivity down to 0.043×10-6 S cm-1 at 18 °C. The limiting conductivity is due to self ionisation
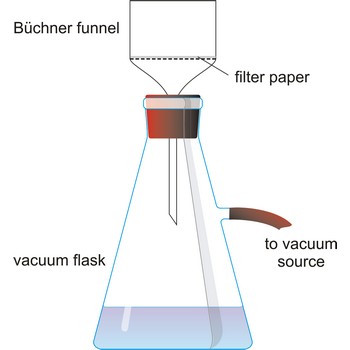
filter flask → boca za odsisavanje
Filter flask, also known as a vacuum flask, is a flask with a side arm to which a vacuum can be applied. It usually have heavy side walls to withstand high vacuum.
Gauss’ law for electrostatics → Gaussov zakon za elektrostatiku
Gauss’ law describes the relation between charge and electric field in static situations, so it is equivalent to Coulomb’s law, which can be derived from Gauss’ law. Gauss’ law states that the net flux of electric field, Φ, through an imaginary closed surface, S, - a Gaussian surface - is equal to the net charge, q, inside that closed surface:
where electric flux Φ through Gaussian surface is given by:
ε0 is the permittivity constant and dS is a surface element.
hafnium → hafnij
Hafnium was discovered by Dirk Coster (Denmark) and Georg Karl von Hevesy (Hungary) in 1923. The origin of the name comes from the Latin name Hafnia meaning Copenhagen. It is silvery, ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Resists alkalis and acids (except HF). Toxic. Metal ignites and burns readily. Hafnium is obtained from mineral zircon or baddeleyite. Used in reactor control rods because of its ability to absorb neutrons.
Hirsch funnel → Hirschov lijevak
Hirsch funnels are essentially smaller Büchner funnels and primarily used to collect a desired solid from a relatively small volume of liquid (1-10 mL). The main difference is that the plate is much smaller, while the walls of the funnel angle outward instead of being vertical. It is named after the German chemist Robert Hirsch (1856-1913).
magnetic permeability → magnetska permeabilnost
Magnetic permeability (μ), also called permeability, is a constant of proportionality that exists between magnetic induction and magnetic field intensity. This constant is equal to approximately μo = 1.257×10-6 H/m in a vacuum.
Magnetic permeability is often expressed in relative, rather than in absolute, terms. If μ represents the permeability of the substance in question, then the relative permeability, μr, is given by:
mass spectrometry → masena spectrometrija
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique in which ions are separated according to the mass/charge (m/e) ratio and detected by a suitable detector.
In a mass spectrometer a sample is ionised and the positive ions produced are accelerated into a high-vacuum region containing electric and magnetic fields. These fields deflect and focus the ions onto a detector. A mass spectrum is thus obtained, consisting of a series of peaks of variable intensity to which m/e values can be assigned. Different molecules can be identified by their characteristic pattern of lines.
metre → metar
Metre (m) is the SI base unit of length.
The meter is the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299 792 458 s.
This definition, adopted by the General Conference on Weights and Measure in October 1983, replaced the 1967 definition based on the krypton lamp.
photomultiplier → fotomultiplikator
Photomultiplier (photomultiplier tube or PMT) is a very versatile and sensitive detector of radiant energy in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. A typical photomultiplier tube consists of a photoemissive cathode (photocathode) followed by focusing electrodes, an electron multiplier (dynode) and an electron collector (anode) in a vacuum tube.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vakuum." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table