degree → stupanj
1. Degree is a unit of temperature on a specified scale. The temperatures of boiling and freezing water are: in the Fahrenheit system 212 and 32 degrees; in the Celsius system 100 and 0 (zero) degrees.
2. Degree is a unit of angular measure. A circle is divided into 360 degrees, represented by the symbol °. Degrees are each divided into 60 minutes. Each minute has 60 seconds. Symbols for degree, minute, and second for plane angle is placed after the numerical value and a no space between the numerical value and the unit symbol (α = 2°3'4").
3. In algebra, the degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. For example, 4x3 + 3x2 + x + 7 have degree 3.
dropping mercury electrode → kapajuća živina elektroda
Dropping mercury electrode (DME) is a working electrode arrangement for polarography in which mercury continuously drops from a reservoir through a capillary tube (internal diameter 0.03 - 0.05 mm) into the solution. The optimum interval between drops for most analyses is between 2 and 5 s. The unique advantage to the use of the DME is that the constant renewal of the electrode surface, exposed to the test solution, eliminates the effects of electrode poisoning.
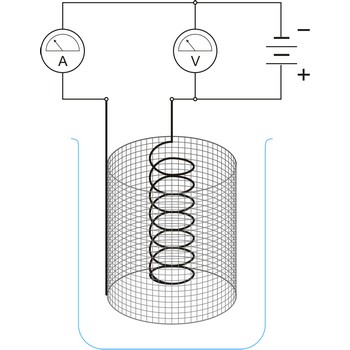
Faradaic reaction → Faradejska reakcija
Faradaic reaction is a heterogeneous charge-transfer reaction occurring at the surface of an electrode.
volt → volt
Volt (V) is the SI derived unit of electric potential. One volt is the difference of potential between two points of an electric conductor when a current of 1 ampere flowing between those points dissipates a power of 1 watt. It was named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745-1827).
electrodeposition → elektrodepozicija
Electrodeposition is a process of depositing solid materials on an electrode surface using electrolysis. It is a somewhat loosely used term that is applied to many technologies. There are a number of metal deposition technologies. However, not only metals but also different compounds can be electrodeposited. This is used most often for the formation of oxides (such as manganese dioxide and lead dioxide) by anodic oxidation of dissolved salts.
electrogravimetry → electrogravimetrija
Electrogravimetry is an electroanalytical technique in which the substance to be determined (usually a metal) is deposited out on an electrode which is weighed before and after the experiment. The potential of the electrode must be carefully chosen to ensure that only the metal do be determined will deposit.
energy → energija
Energy (E, U) is the characteristic of a system that enables it to do work. Like work itself, it is measured in joules (J).
The internal energy of a body is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy of its component atoms and molecules.
Potential energy is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy).
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is usually defined as the work that will be done by a body possessing the energy when it is brought to rest. For a body of mass m having a speed v, the kinetic energy is mv2/2. Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
In an isolated system energy can be transferred from one form to another but the total energy of the system remains constant.
fugacity → fugacitet
Fugacity (f) is a thermodynamic function used in place of partial pressure in reactions involving real gases and mixtures. For a component of a mixture, it is defined by
where μ is the chemical potential.
The fugacity of a gas is equal to the pressure if the gas is ideal. The fugacity of a liquid or solid is the fugacity of the vapour with which it is in equilibrium. The ratio of the fugacity to the fugacity in some standard state is the activity.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Uvjetni elektrodni potencijal." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table