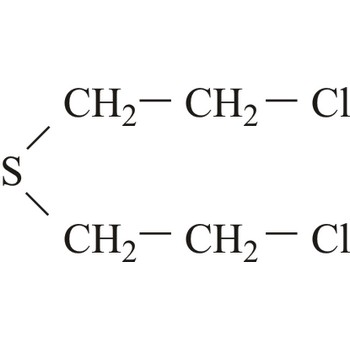activated charcoal → aktivni ugljen
Activated charcoal or activated carbon is charcoal that has been activated for adsorption by steaming or by heating in a vacuum. Charcoal is obtained by burning wood, nutshells, coconut husks or other materials. Charcoal becomes activated by heating it with steam to approximately 1000 °C in the absence of oxygen.
The chemical nature of amorphous carbon, combined with a high surface area makes it an ideal medium for the adsorption of organic chemicals. A single gram of such material can have 400 m2 to 1 200 m2 square meters of surface area. Activated charcoal is widely used to decolorize liquids, recover solvents, and remove toxins from water and air.
coal → ugljen
Coal is a black or brownish-black, combustible sedimentary rock, with 30 % (lignite) to 98 % (anthracite) carbon by weight, mixed with various amounts of water and small amounts of sulfur and nitrogen compounds. It is formed from plant matter that decayed in swamps and bogs that has been compressed and altered by geological processes over millions of years. Coal is primarily used as a fuel.
gas thermometer → plinski termometar
Gas thermometer is a device for measuring temperature in which the working fluid is a gas.
pit coal → kameni ugljen
Pit coal is natural black coal that has a carbon content of 75 %-90 %. It is an important raw material in organic industry
gas liquefying → ukapljivanje plinova
In order to achieve transition of a gas into liquid state it is necessary to lower its temperature, or decrease its volume, or increase its pressure. Above the critical temperature it is impossible to liquefy a gas. When liquefying a gas by Linde’s procedure, dampening or Joule-Thomson’s effect is used. First, the compressed air from the compressor is cooled with cooling water, the cooled air expands at a lower pressure in the dampening valve at which it cooled. The cooled air now returns to the compressor, cooling down the expanding air. By repeating this process the air is cooled enough to transit to the liquid state.
universal gas constant → univerzalna plinska konstanta
Universal gas constant R has the value of 8.314 472(15) J K-1 mol-1. It corresponds to the volume work performed by one mole of gas heated by 1 K at standard pressure.
ideal gas law → jednadžba stanja idealnog plina
The generalized ideal gas law is derived from a combination of the laws of Boyle and Charles. Ideal gas law is the equation of state
which defines an ideal gas, where p is pressure, V molar volume, T temperature, and R the molar gas constant (8.314 JK-1mol-1).
mustard agent → plikavac
Mustard agents are usually classified as blistering agents owing to the similarity of the wounds caused by these substances resembling burns and blisters. However, since mustard agents also cause severe damage to the eyes, respiratory system and internal organs, they should preferably be described as blistering and tissue-injuring agents. Normal mustard agent (yperite), 1,1-thio-bis-[2-chloroethane], reacts with a large number of biological molecules. The effect of mustard agent is delayed and the first symptoms do not occur between 2-24 hours after exposure. At room temperature, mustard agent is a liquid with low volatility and is very stable during storage.
fossil fuel → fosilno gorivo
Fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) are the fuels used by man as a source of energy. They are formed from the remains of living organisms and all have a high carbon or hydrogen content. They have value as fuels on the exothermic oxidation of carbon to form carbon dioxide
and the oxidation of hydrogen to form water
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ugljeni plin." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table