thermal conductivity → toplinska vodljivost
Thermal conductivity (Λ) is rate of heat flow divided by the area and by the temperature gradient.
waste water → otpadna voda
Waste waters are waters which pour down from housing, public or industrial plants and are polluted with mineral and organic substances and microorganisms.
heavy water → teška voda
Water molecules are composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O). If the hydrogen atoms of a water molecule are replaced by deuterium atoms, the result is heavy water (D2O). Deuterium differs from hydrogen by having one neutron in the nucleus of the atom. There is approx. one part in 5000 D2O in normal water and it can be concentrated by electrolysis. Heavy water has a higher boiling point (101.4 °C) and melts at 3.6 °C. Heavy water is 20/18=1.11 times heavier than ordinary water.
hydrogen → vodik
Hydrogen was discovered by Sir Henry Cavendish (England) in 1766. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words hydro and genes meaning water and generate. It is colourless, odourless gas, burns and forms explosive mixtures in air. Reacts violently with oxidants. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. Commercial quantities of hydrogen are produced by reacting superheated steam with methane or carbon. In lab work from reaction of metals with acid solutions or electrolysis. Most hydrogen is used in the production of ammonia and in metal refining. Also used as fuel in rockets. Its two heavier isotopes (deuterium and tritium) used respectively for nuclear fusion.
hydrogen bond → vodikova veza
Hydrogen is a bond formed by a hydrogen atom to an electronegative atom, and is denoted by dashed lines H-X---H-B. A hydrogen atom covalently bound to an oxygen (electronegative atom) has a significant positive charge and can form a weak bond to another electronegative atom.
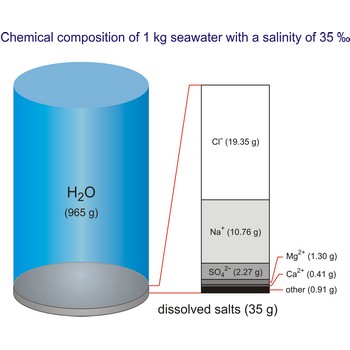
salt water → slana voda
Salt water is the water of the sea and the ocean. This water contains a relatively high percentage of dissolved salt (about 35 g of salt per 1 000 g of sea water.). About 90 % of that salt would be sodium chloride, or ordinary table salt.
The salinity of ocean water varies. It is affected by such factors as melting of ice, inflow of river water, evaporation, rain, etc.
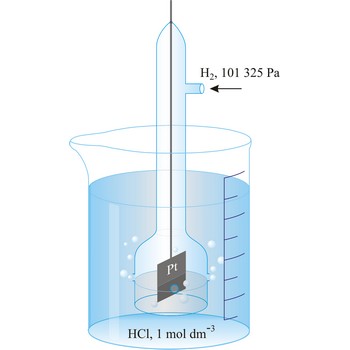
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
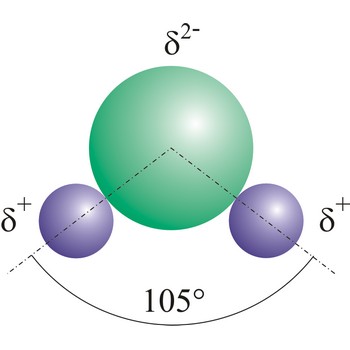
water → voda
Water (H2O) (dihydrogen oxide) is a binary compound that occurs at room temperature as a clear colorless odorless tasteless liquid; freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C. Water is a chemical compound which is essential for living organisms and it is widely used as a solvent.
water gas → vodeni plin
Water gas (blue gas, synthesis gas) is a fuel gas used in industrial synthesis of organic chemicals, and in welding, glassmaking, and other high-temperature industrial applications. Water gas is made by passing steam over a bed of hot coal or coke. It mainly consists of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2), contaminated with small amounts of CO2, N2, CH4, and O2.
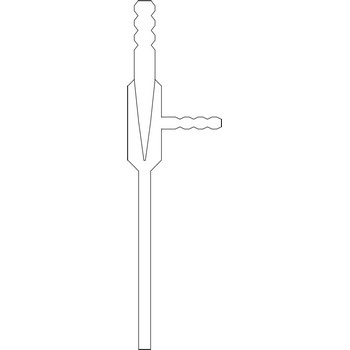
water jet vacuum pump → vodena sisaljka
The water jet vacuum pump or vacuum aspirator is one of the most popular devices that produces vacuum in laboratories. The rapid flow of water through the device creates a vacuum in a side-arm that is connected to a vacuum application such a Buchner flask. The water jet vacuum pump creates a vacuum by means of Venturi effect named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822). The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. Water jet pumps are manufactured of glass, plastic or metal, depending on the conditions in which they are used.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Tvrdoća vode." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table