dipole → dipol
Dipole is a pair of separated opposite electric charges. Electric dipole is an assemblage of atoms or subatomic particles having equal electric charges of opposite sign separated by a finite distance. In the case of HCl, the electrons are attracted towards the more electronegative chlorine atom.
plastic sulphur → plastični sumpor
Plastic sulphur is the shape of sulphur which emerges when hot, liquid sulphur pours out in the water. It can be stretched in long fibres is unstable unstable. It easily solidifies.
polyvalent element → polivalentni elementi
Polyvalent element is a molecule which having more than one valence, for example oxygen is a divalent in H2O, nitrogen is a trivalent in NH3, carbon is a tetravalent in methane (CH4).
primary alcohol → primarni alkohol
Primary alcohols are alcohols where the hydroxyl group is attached to a primary carbon atom. Thus, it has the general structure, RCH2OH, where R is a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group.
dipole molecule → dipolna molekula
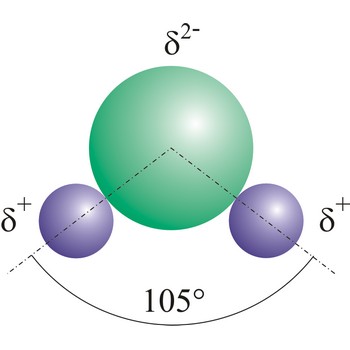
Dipole molecules are created when mutual electronic pair at covalent bond is asymmetrical. If different atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, which can have different electron affinity, then the the atom with greater electron affinity will attract the electron pairs more strongly. In this way an asymmetrical distribution of negative charge appears in a molecule, so one part of the molecule becomes relatively negatively (the one closer to the electron pair) and the other becomes relatively positively charged.
dissociation → disocijacija
Dissociation is the process by which a chemical combination breaks up into simpler constituents as a result of either added energy (dissociated by heat), or the effect of a solvent on a dissolved polar compound (electrolytic dissociation). It may occur in the gaseous, solid, or liquid state, or in a solution.
An example of dissociation is the reversible reaction of hydrogen iodide at high temperatures
The term dissociation is also applied to ionisation reactions of acids and bases in water. For example
which is often regarded as a straightforward dissociation into ions
reactive metal → reaktivni metal
Reactive metals are metals that readily combine with oxygen at elevated temperatures to form very stable oxides, for example titanium, zirconium, and beryllium. Reactive metals may also become embrittled by the interstitial absorption of oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
relative humidity → relativna vlažnost
Relative humidity is the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapour in air to the saturation vapour pressure of water at the same temperature, expressed as a percentage.
reverse osmosis → reverzna osmoza
Reverse osmosis is the method used for obtaining freshwater from saltwater. The process uses a semi-permeable membrane through which pure water and not the salts will pass. The saltwater must be pressurised to approximately 25 bar, which makes it operationally expensive to produce large quantities of fresh water by this method.
salinisation → salinizacija
Salinisation is the increase in salinity of fresh surface and ground water supplies.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Tvrdoća vode." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table