plutonium → plutonij
Plutonium was discovered by Glenn T. Seaborg, Edwin M. McMillan, J. W. Kennedy and A. C. Wahl (USA) in 1940. Named after the planet Pluto. It is silvery-white, extremely radioactive artificially produced metal. Reacts with oxygen and acids; resists alkalis. Attacked by steam. Highly toxic. Plutonium is found rarely in some uranium ores. Made by bombarding uranium with neutrons. Used in bombs and reactors. Small quantities are used in thermo-electric generators.
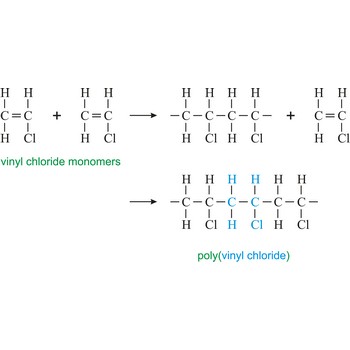
polyvinyl chloride → polivinil klorid
Poly(vinyl chloride) or the PVC is hard and resistant homopolymer produced by the polymerization of the gas vinyl chloride [CH2CHCl]. The pure polymer is hard, brittle and difficult to process, but it becomes flexible when plasticizers are added. After mixing with plasticizers, stabilizers, and pigments, the resin may be fabricated by techniques such as calendering, molding, or extrusion into flexible articles such as raincoats, shower curtains, and packaging films. The resin is not plasticized for use in making rigid products such as water pipe, plumbing fittings, and phonograph records.
zero law of thermodynamics → nulti zakon termodinamike
Zero law of thermodynamics states: If some body A is in thermal equilibrium with body B and with body C, then bodies B and C are also in thermal equilibrium.
potential energy → potencijalna energija
Potential energy (Ep) is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy). Gravitational potential energy is the energy associated with the state of separation between bodies that attracts each other via gravitational force. Elastic potential energy is the energy associated with the state of compression or extension of an elastic object. Thermal energy is associated with the random motions of atoms and molecules in a body.
Prandtl number → Prandtlova značajka
Prandtl number (Pr) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where η is viscosity, ρ is density, and a is thermal diffusivity.
protactinium → protaktinij
Protactinium was discovered by Otto Hahn (Germany) and Lise Meitner (Austria) in 1917. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word protos meaning first. It is very rare, silvery-white, extremely radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; reacts with oxygen and acids. Attacked by steam. Highly radiotoxic. Protactinium is extremely toxic and must be handled with great care. Protactinium does not occur in nature. Found among fission products of uranium, thorium and plutonium.
Rayleigh number → Rayleighova značajka
Rayleigh number (Ra) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where l is length, g is acceleration of gravity, α is cubic expansion coefficient, T is temperature, ρ is density, η is viscosity, and a is thermal diffusivity.
rhenium → renij
Rhenium was discovered by Walter Noddack, Ida Tacke and Otto Berg (Germany) in 1925. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Rhenus meaning river Rhine. It is rare and costly, dense, silvery-white metal. Tarnishes in moist air. Resists corrosion and oxidation. Dissolves in nitric and sulfuric acids. Has a very high melting point. Rhenium is found in small amounts in gadolinite and molybdenite. Mixed with tungsten or platinum to make filaments for mass spectrographs. Its main value is as a trace alloying agent for hardening metal components that are subjected to continuous frictional forces.
samarium → samarij
Samarium was discovered by Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran (France) in 1879. Named after the mineral samarskite. It is silvery rare earth metal. Stable in dry air. Oxide coating forms on surfaces exposed to moist air. Metal ignites and burns readily. Reacts with water. Samarium is found with other rare earths in monazite sand. It is used in the electronics and ceramics industries. It is easily magnetized and very difficult to demagnetise. This suggests important future applications in solid-state and superconductor technologies.
superfluid helium → superfluidni helij
Superfluidity in helium-4 was discovered in 1938 by the Soviet physicist Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa. Helium-4 exhibits superfluidity when it is cooled below 2.18 K (-270.97 C), which is called the lambda (λ) point. At these temperatures, helium-4 exhibits the characteristics of two distinct fluids, one of which appears to flow without friction. An extensive series of experiments showed that in this state of helium, called helium II (He II), there is an apparent enormous rise in heat conductivity, at an increase rate of about three million. Another unusual property of He II is its mobile, rapid flow through capillaries or over the rim of its containment vessel as a thin film that exhibits no measurable viscosity and appears unaffected by the forces of gravity or evaporation and condensation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Toplinski otpor." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table