system → sustav
System is the region under consideration, as distinguished from the rest of the universe (the environment). Systems may be separated from environments by boundaries that prevent the transfer of mass (a closed system), of heat (an adiabatic system), or of any energy (an isolated system). Systems that exchange mass with the environment are open systems.
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
non-metal → nemetal
Non-metals are defined as elements that are not metals.
Their physical properties generally include:
- They are poor conductors.
- They are brittle, not ductile in their solid state.
- They show no metallic lustre.
- They may be transparent or translucent.
- They have low density.
- They form molecules which consists of atoms covalently bonded; the noble gases are monoatomic.
Their chemical properties are generally:
- They usually have four to eight valence electrons.
- They have high electron affinities (except the noble gases)
- They are good oxidising agents (except the noble gases)
- They have hydroxides which are acidic (except the noble gases)
- They are electronegative.
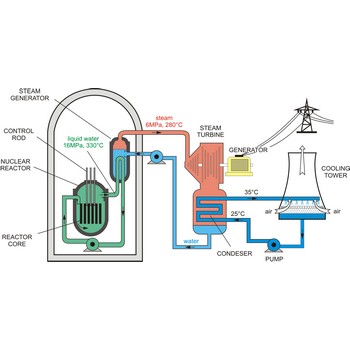
nuclear reactor → nuklearni reaktor
Nuclear reactor is an assembly of fissionable material (uranium-235 or plutonium-239) designed to produce a sustained and controllable chain reaction for the generation of electric power.
The essential components of a nuclear reactor are:
- The core, metal rods containing enough fissionable material to maintain a chain reaction at the necessary power level (as much as 50 t of uranium may be required).
- A source of neutrons to initiate the reaction (such as a mixture of polonium and beryllium)
- A moderator to reduce the energy of fast neutrons for more efficient fission (material such as graphite, beryllium, heavy water, and light water are used)
- A coolant to remove the fission-generated heat (water, sodium, helium, and nitrogen may be used)
- A control system such as rods of boron or cadmium that have high capture cross sections (to absorb neutrons)
- Adequate shielding, remote-control equipment, and appropriate instrumentation are essential for personnel safety and efficient operation.
Nusselt number → Nusseltova značajka
Nusselt number (Nu) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechan-ics, defined by
where h is coefficient of heat transfer, l is length, and k is thermal conductivity.
Peclet number → Pecletova značajka
Péclet number (Pe) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where v is velocity, l is length, and a is thermal diffussivity.
plastic → plastika
Plastic is a material that can be shaped by the application of heat or pressure. Most are based on synthetic polymers although some are the product of natural substances (such as cellulose derivatives, but excluding the rubbers.). They are usually light and permanent solids, being also heat and electric isolators. If the materials soften again when reheated, they are said to be thermoplastic. If, after fashioning, they resist further applications of heat, they are said to be thermoset.
potential energy → potencijalna energija
Potential energy (Ep) is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy). Gravitational potential energy is the energy associated with the state of separation between bodies that attracts each other via gravitational force. Elastic potential energy is the energy associated with the state of compression or extension of an elastic object. Thermal energy is associated with the random motions of atoms and molecules in a body.
Prandtl number → Prandtlova značajka
Prandtl number (Pr) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where η is viscosity, ρ is density, and a is thermal diffusivity.
Rayleigh number → Rayleighova značajka
Rayleigh number (Ra) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where l is length, g is acceleration of gravity, α is cubic expansion coefficient, T is temperature, ρ is density, η is viscosity, and a is thermal diffusivity.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Toplina hidratacije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table