equivalence point → točka ekvivalencije
Eequivalence point is the point in a titration when enough titrant has been added to react completely with the analyte.
critical point → kritična točka
In general, critical point is the point on the phase diagram of a two-phase system at which the two coexisting phases have identical properties and therefore represent a single phase. At the liquid-gas critical point of a pure substance, the distinction between liquid and gas vanishes, and the vapour pressure curve ends. The coordinates of this point are called the critical temperature and critical pressure. Above the critical temperature it is not possible to liquefy the substance.
point-like object → materijalna točka
Point-like object is an expression, usual in kinematics: a point-like object (or a particle) is an object with dimensions, which can be neglected while considering its motion.
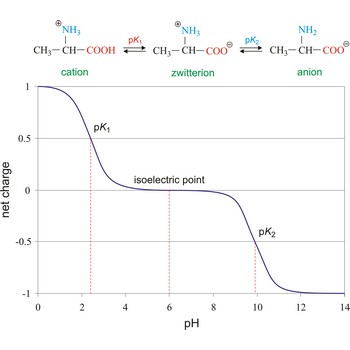
isoelectric point → izoelektrična točka
Isoelectric point (pI or IEP) is the pH of a solution or dispersion at which the net charge on the molecules or colloidal particles is zero. In electrophoresis there is no motion of the particles in an electric field at the isoelectric point. The net charge (the algebraic sum of all the charged groups present) of any amino acid, peptide or protein, will depend upon the pH of the surrounding aqueous environment. For example, alanine can have a charge of +1, 0, or -1, depending on the pH of the solution in which it is dissolved.
triple point → trojna točka
Triple point is the point in p,T space where the solid, liquid, and gas phases of a substance are in thermodynamic equilibrium.
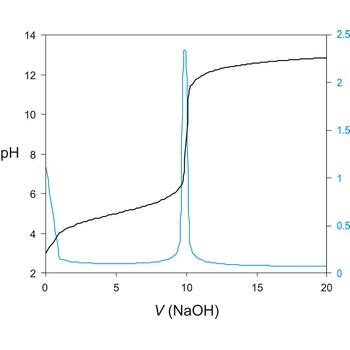
potentiometric titration → potenciometrijska titracija
Potentiometric titration is a volumetric method in which the potential between two electrodes is measured (referent and indicator electrode) as a function of the added reagent volume. Types of potentiometric titrations for the determination of analytes in photoprocessing solutions include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric.
Potentiometric titrations are preferred to manual titrations, since they are more accurate and precise. They are also more easily adapted to automation, where automated titration systems can process larger volumes of samples with minimal analyst involvement.
A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The part of the curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalence point of the titration. The first derivative, ΔE/ΔV, is the slope of the curve, and the endpoint occurs at the volume, V', where ΔE/ΔV has the maximum value.
mass-energy equivalence → ekvivalencija mase i energije
In the special theory of relativity Einstein demonstrated that neither mass nor energy were conserved separately, but that they could be traded one for the other and only the total "mass-energy" was conserved. The relationship between the mass and the energy is contained in what is probably the most famous equation in science,
Where m is the mass of the object and c is the velocity of light. Cockcroft and Walton (1932) are routinely credited with the first experimental verification of mass-energy equivalence.
acceleration → akceleracija
If a point-like object undergoes a change in velocity Δv=vf-vi in time Δt=tf-ti (indexes i and f stand for initial and final instant as well as for initial and final velocity) its average acceleration, a is defined as
The instantaneous acceleration, a, is obtained from the average acceleration by shrinking the time interval Δt towards zero. The average acceleration approaches a limiting value, which is the acceleration of a given instant:
Acceleration is a vector quantity. SI unit for acceleration is m s-2.
acid-base titration → kiselo-bazna titracija
Acid-base titration is an analytical technique in volumetric analysis, where an acid of known concentration is used to neutralise a known volume of a base, and the observed volume of the acid required is used to determine the unknown concentration of the base. An acid-base indicator is used to determine the end-point of the titration.
allotropy → alotropija
Allotropy (Gr. allos, other, and tropos, manner) is the phenomenon of an element existing in two or more physical forms in the same physical state. The difference between the forms involves either crystaline structure (white, red and black phosphorus), the number of atoms in the molecule of a gas (diatomic oxygen and triatomic ozone), or the molecular structure of a liquid (liquid helium an helium II).
In some cases, the allotropes are stable over a temperature range, with a definite transition point at which one changes into the other. For instance, tin has two allotropes: white (metallic) tin stable above 13.2 °C and grey (nonmetallic) tin stable below 13.2 °C. This form allotropy is called enantiotropy. Form of allotropy, in which there is no transition temperature at which the two are in equilibrium, is called monotropy.
Allotropy does not apply to the substance existing in different physical states as, for example, when ice melts and changes from solid ice to liquid water.
Allotropy is generally restricted to describing polymorphic behaviour in elements, while polymorphism may refer to any material having multiple crystal structures.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Točka ekvivalencije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table