Ostwald’s process → Ostwaldov proces
Ostwald’s process is a process by which the nitric acid can be obtained in three degrees. In the first stage ammonia and oxygen react (with platinum-rhodium as a catalyst), whereby the nitrogen monoxide and water emerge
In the second stage nitrogen monoxide reacts with oxygen whereby nitrogen dioxide emerges
and in the third stage nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water, in the presence of air, giving the nitric acid
palladium → paladij
Palladium was discovered by William Hyde Wollaston (England) in 1803. Named after the asteroid Pallas which was discovered at about the same time and from the Greek name Pallas, goddess of wisdom. It is soft, malleable, ductile, silvery-white metal. Resists corrosion; dissolves in oxidizing acids. Absorbs hydrogen. Metal dust is combustible. Palladium is obtained with platinum, nickel, copper and mercury ores. Used as a substitute for silver in dental items and jewellery. The pure metal is used as the delicate mainsprings in analog wristwatches. Also used in surgical instruments and as catalyst.
platinum → platina
Platinum was discovered by Antonio de Ulloa (South America) in 1735. The origin of the name comes from the Spanish word platina meaning silver. It is rare, very heavy, soft, silvery-white metal. Resists oxygen and water. Platinum is produced from deposits of native, or elemental. Used in jewellery, to make crucible and special containers and as a catalyst. Used with cobalt to produce very strong magnets. Also to make standard weights and measures. Resists corrosion and acid attacks except aqua regia.
poison → otrov
Poisons are substance, which upon contact or being introduced into an organism, impair or prevent normal metabolic processes from taking place, thus altering the normal functioning of organs or tissues.
Poisons are molecules or material that tends to collect on a catalyst surface, blocking access to active sites or destroying their activities.
Poisons are substance that can reduce a nuclear reaction by absorbing neutrons, thereby preventing more fission. If enough poisons are present in a reactor core, the chain reaction will die out.
rhodium → rodij
Rhodium was discovered by William Hyde Wollaston (England) in 1804. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word rhodon meaning rose. It is hard, silvery-white metal. Inert in air and acids. Reacts with fused alkalis. Rhodium is obtained as a by-product of nickel production. Used as a coating to prevent wear on high quality science equipment and with platinum to make thermocouples.
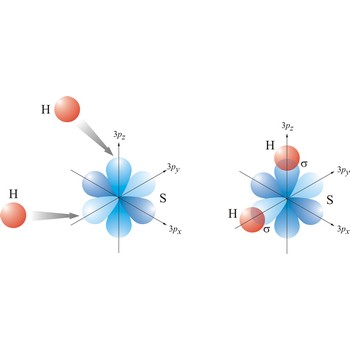
sigma bond → sigma veza
Most single bonds are sigma bonds (σ-bond). In the valence bond theory, a sigma bond is a valence bond that is symmetrical around the imaginary line between the bonded atoms.
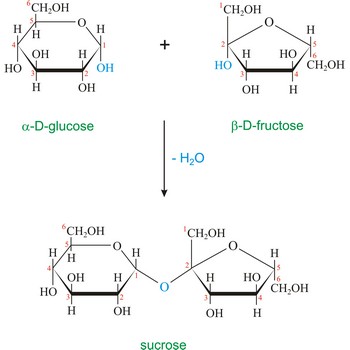
sucrose → saharoza
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
tellurium → telurij
Tellurium was discovered by Franz Joseph Muller von Reichstein (Romania) in 1782. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word tellus meaning earth. It is silvery-white, brittle semi-metal. Unreactive with water or HCl; dissolves in HNO3; burns in air or oxygen. Tellurium is obtained as a by-product of copper and lead refining. Used to improve the machining quality of copper and stainless steel products and to colour glass and ceramics. Also in thermoelectric devices. Some is used in the rubber industry and it is a basic ingredient in manufacturing blasting caps.
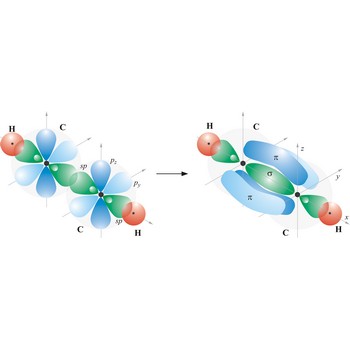
triple bond → trostruka veza
Triple bond. (≡) is a covalent bond that involves 3 bonding pairs. In the valence bond theory, one of the bonds in a triple bond is a sigma bond and the other two are pi bonds. For example, the central bond in acetylene is a triple bond: H-C≡C-H.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Teorije katalize." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table