relative humidity → relativna vlažnost
Relative humidity is the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapour in air to the saturation vapour pressure of water at the same temperature, expressed as a percentage.
reverse osmosis → reverzna osmoza
Reverse osmosis is the method used for obtaining freshwater from saltwater. The process uses a semi-permeable membrane through which pure water and not the salts will pass. The saltwater must be pressurised to approximately 25 bar, which makes it operationally expensive to produce large quantities of fresh water by this method.
salinisation → salinizacija
Salinisation is the increase in salinity of fresh surface and ground water supplies.
electrode of the third kind → elektroda trećeg reda
Electrode of the third kind is a metal electrode assembly with the equilibrium potential being a function of the concentration of a cation, other than the cation of the electrode metal, in the solution. The assembly consists of a metal in contact with two slightly soluble salts (one containing the cation of the solid metal, the other the cation to be determined, with both salts having a common anion) immersed in a solution containing a salt of the second metal (e.g., zinc metal--zinc oxalate--calcium oxalate--calcium salt solution). The potential of the metal is controlled by the concentration of its cation in the solution, but this is controlled by the anion concentration in the solution through the solubility product of the slightly soluble metal salt, which, in turn is controlled by the concentration of the cation of the second slightly soluble salt. These electrodes are very sluggish and unstable due to a series of equilibria to be established to produce a stable potential.
electrode potential → elektrodni potencijal
Electrode potential is defined as the potential of a cell consisting of the electrode in question acting as a cathode and the standard hydrogen electrode acting as an anode. Reduction always takes place at the cathode, and oxidation at the anode. According to the IUPAC convention, the term electrode potential is reserved exclusively to describe half-reactions written as reductions. The sign of the half-cell in question determines the sign of an electrode potential when it is coupled to a standard hydrogen electrode.
Electrode potential is defined by measuring the potential relative to a standard hydrogen half cell
The convention is to designate the cell so that the oxidised form is written first. For example
The e.m.f. of this cell is
By convention, at p(H2) = 101325 Pa and a(H+) = 1.00, the potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is 0.000 V at all temperatures. As a consequence of this definition, any potential developed in a galvanic cell consisting of a standard hydrogen electrode and some other electrode is attributed entirely to the other electrode
sand filtration → pješčana filtracija
Sand filtration is a frequently used and very robust method of removing suspended solids from water. The filtration medium consists of a multiple layer of sand with a variety in size and specific gravity. Sand filters can be supplied in different sizes and materials, both hand operated and fully automatically.
solvation → solvatacija
Solvation is the process by which solvent molecules surround and interact with solute ions or molecules.
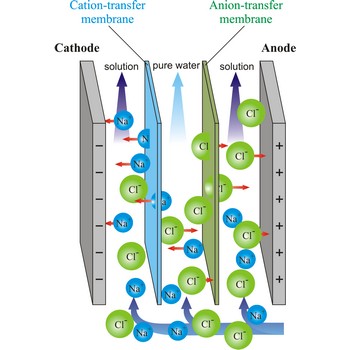
electrodialysis → elektrodijaliza
Electrodialysis is a procedure of dialysis accelerated with an electric field. Dialyser is divided into three sections. Solution flows through the middle section, between two semipermeable membranes alternately to positive ions and negative ions. An electrodes are placed in the neighbouring sections. Under the influence of electric field, positive ions will travel towards the cathode (the negative electrode), and negative ions towards the anode (the positive electrode), whereby travelling of ions through the membrane is accelerated. In this way, the feed water is separated into two streams: one of pure water and the other of more concentrated solution.
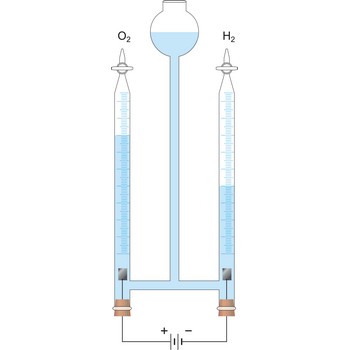
electrolysis → elektroliza
Electrolysis is the decomposition of a substance as a result of passing an electric current between two electrodes immersed in the sample.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Teška voda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table