indium → indij
Indium was discovered by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymus Theodor Richter (Germany) in 1863. Named after the indicum (colour indigo), the colour it shows in a spectroscope. It is rare, very soft, silver-white metal. Stable in air and water. Dissolves in acids. Metal can ignite and burn. Indium is found in certain zinc ores. Used to coat high speed bearings and as an alloy that lowers the melting point of other metals. Relatively small amounts are used in dental items and in electronic semiconductors.
iodine → jod
Iodine was discovered by Bernard Courtois (France) in 1811. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word iodes meaning violet. It is shiny, black, non-metallic solid with characteristic odour. Sublimes easily and as a gas it is violet and intensely irritating to the eyes, nose and throat. Iodine occurs on land and in the sea in sodium and potassium compounds. Required in small amounts by humans. Once used as an antiseptic, but no longer due to its poisonous nature.
iridium → iridij
Iridium was discovered by Smithson Tennant (England) in 1803. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word iris, meaning rainbow, because its salts are highly colored. It is heavy, brittle, white metal. Unreactive in air, water and acids. Attacked by fused NaOH. Metal ignites and burns readily. Iridium is found in gravel deposits with platinum. Used with osmium to tip gold pen points, to make crucible and special containers. Also to make alloys used for standard weights and measures and heat-resistant alloys. Also as hardening agent for platinum.
iron → željezo
Iron has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word ferrum meaning iron. It is malleable, ductile, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces form red-brown oxides. Forms very strong alloys (steel). Ferromagnetic. Metal dust flammable. Fourth most abundant element in the earth’s crust. Iron is obtained from iron ores. Pure metal produced in blast furnaces by layering limestone, coke and iron ore and forcing hot gasses into the bottom. This heats the coke red hot and the iron is reduced from its oxides and liquefied where it flows to the bottom. Iron is the most common metal in human society. More than 90 % of all metal refined in the world is iron. Used in steel and other alloys. It is the chief constituent of hemoglobin which carries oxygen in blood vessels. Its oxides are used in magnetic tapes and disks.
krypton → kripton
Krypton was discovered by Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers (England) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word kryptos meaning hidden. It is colourless, odourless rare noble gas. Reacts only with fluorine. Krypton is obtained from production of liquid air. Used in lighting products. Some is used as inert filler-gas in incandescent bulbs. Some is mixed with argon in fluorescent lamps. The most important use is in flashing stroboscopic lamps that outline airport runways.
lanthanum → lantan
Lanthanum was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1839. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word lanthanein meaning to lie hidden. It is soft, silvery-white, malleable, ductile metal. Readily tarnishes in air. Reaction with water releases hydrogen gas. Metal ignites and burns readily. Reacts with oxidants. Lanthanum is found with rare earths in monazite and bastnasite. Monazite sand typical contains 25 % lanthanum. It is used in the electrodes of high-intensity, carbon-arc lights. Because it gives glass refractive properties, it is used in expensive camera lenses.
lawrencium → lawrencij
Lawrencium was discovered by Albert Ghiorso, Torbjorn Sikkeland, Almon E. Larsh and Robert M. Latimer (USA) in 1961. Named in honour of Ernest O. Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Lawrencium was produced by bombarding a mixture of three isotopes of californium with boron-10 and boron-11 ions. Eight isotopes of lawrencium have been synthesized to date, with the longest-lived being lawrencium-256, which has a half-life of about 30 seconds.
lead → olovo
Lead has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word plumbum meaning liquid silver. It is very soft, highly malleable and ductile, blue-white shiny metal. Tarnishes in moist air; stable in oxygen and water. Dissolves in nitric acid. Compounds toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Danger of cumulative effects. Lead is found most often in ores called galena or lead sulfide (PbS). Used in solder, shielding against radiation and in batteries.
limestone → vapnenac
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate in the form of the mineral calcite.. Some 10 % to 15 % of all sedimentary rocks are limestones. Limestone is usually organic, but it may also be inorganic. Calcium carbonate may have been directly precipitated from the sea-water or by the lithification of coral reefs, marine organism shells, or marine organism skeletons.
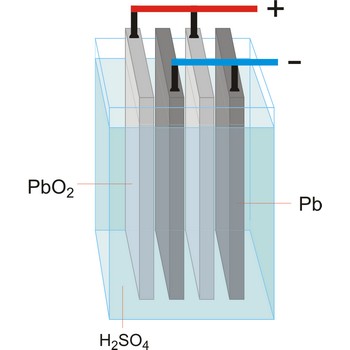
lead-acid battery → olovni akumulator
Lead-acid battery is a electrical storage device that uses a reversible chemical reaction to store energy. It was invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. Lead-acid batteries are composed of a lead(IV) oxide cathode, a sponge metallic lead anode and a sulphuric acid solution electrolyte.
In charging, the electrical energy supplied to the battery is changed to chemical energy and stored. The chemical reaction during recharge is normally written:
In discharging, the chemical energy stored in the battery is changed to electrical energy. During discharge, lead sulfate (PbSO4) is formed on both the positive and negative plates. The chemical reaction during discharge is normally written:
Lead acid batteries are low cost, robust, tolerant to abuse, tried and tested. For higher power applications with intermittent loads however, they are generally too big and heavy and they suffer from a shorter cycle life.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Svjetlosna godina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table