zeta potential → zeta potencijal
Zeta potential (ζ) is the potential across the interface of all solids and liquids. Specifically, the potential across the diffuse layer of ions surrounding a charged colloidal particle, which is largely responsible for colloidal stability. Also called electrokinetic potential.
half-wave potential → poluvalni potencijal
Half-wave potential (E1/2) is a potential at which polarographic wave current is equal to one half of diffusion current (id). In a given supporting electrolyte, the half-wave potential is unique for each element and its different valence states and chemical forms. Observation of a current peak at a specific half-wave potential therefore identifies the chemical species producing the current.
Lennard-Jones potential → Lennard-Jonesov potencijal
The Lennard-Jones potential (or 12-6 potential) is a mathematically simple model that describes the interaction between two non-bonded and uncharged atoms (known as the van der Waals interaction). It was first proposed in 1924 by British physicist Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones (1894-1954). The Lennard-Jones Potential is given by the following equation
V(r) = 4e[(sigma/r)12-(sigma/r)6)]
where V is the intermolecular potential between the two atoms or molecules, ε is the well depth and a measure of how strongly the two particles attract each other, σ is the distance at which the intermolecular potential between the two particles is zero, r is the distance of separation between centres of both particles.
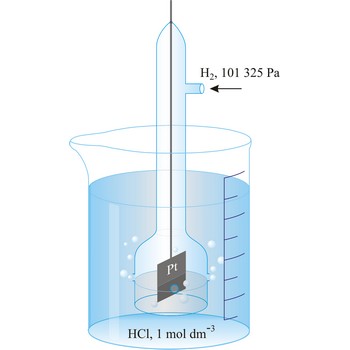
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
electrochemical series → elektrokemijski niz
Electrochemical series is a series of chemical elements arranged in order of their standard electrode potentials. The hydrogen electrode
is taken as having zero electrode potential. An electrode potential is, by definition, a reduction potential.
Elements that have a greater tendency than hydrogen to lose electrons to their solution are taken as electropositive; those that gain electrons from their solution are below hydrogen in the series and are called electronegative.
The series shows the order in which metals replace one another from their salts; electropositive metals will replace hydrogen from acids.
standard mean ocean water → standardna prosječna oceanska voda
Standard mean ocean water (SMOW) is a standard sample of pure water of accurately known isotopic composition which is maintained by the International Atomic Energy Agency. It is used for precise calibration of density and isotopic composition measurements.
potential energy → potencijalna energija
Potential energy (Ep) is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy). Gravitational potential energy is the energy associated with the state of separation between bodies that attracts each other via gravitational force. Elastic potential energy is the energy associated with the state of compression or extension of an elastic object. Thermal energy is associated with the random motions of atoms and molecules in a body.
standard deviation → standardna devijacija
Standard deviation (σ) is a measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. Standard deviation is a statistical term that measures the amount of variability or dispersion around an average
Suppose there are many measurements of a quantity presumed to be similar, like the size of peas in a pod. If the number of readings for each size were plotted, a bell-shaped curve would probably result, with a few small and large peas and most clustered around the average size. Around two-thirds of all measurements fall in the range spanned by the standard deviation, a measure of the spread.
calomel electrode → kalomel elektroda
Calomel electrode is a type of half cell in which the electrode is mercury coated with calomel (Hg2Cl2) and the electrolyte is a solution of potassium chloride and saturated calomel. In the calomel half cell the overall reaction is
Table: Dependence of potential of calomel electrode upon temperature and concentration of KCl according to standard hydrogen electrode
| Potential vs. SHE / V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| t / °C | 0.1 mol dm-3 | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.3362 | 0.254 | 0.2511 |
| 20 | 0.3359 | 0.252 | 0.2479 |
| 25 | 0.3356 | 0.250 | 0.2444 |
| 30 | 0.3351 | 0.248 | 0.2411 |
| 35 | 0.3344 | 0.246 | 0.2376 |
negative pole → negativan pol
Negative pole is that half-cell in electrochemical cell that has the most negative electrode potential.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Standardni elektrodni potencijal." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table