standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
Tafel plot → Tafelov dijagram
Tafel plot is the graph of the logarithm of the current density j against the overpotential η in electrochemistry in the high overpotential limit. An electrode when polarised frequently yields a current potential relationship over a region which can be approximated by:
where η is change in open circuit potential, i is the current density, B and i0 is constants. B is known as the Tafel Slope. If this behaviour is observed a plot of the semilogarithmic components is known as the Tafel line and the diagram is called the Tafel diagram.
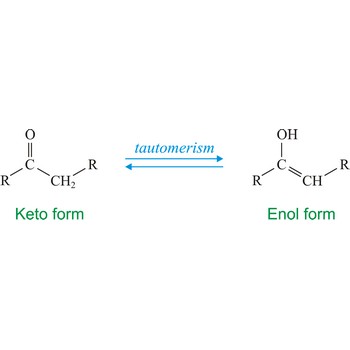
tautomerism → tautomerija
Tautomerism refers to equilibrium between two different structures of the same compound. Usually the tautomers differ in the point of attachment of a hydrogen atom. One of the most common examples of a tautomeric system is the equilibrium between a ketone (keto) and aldehyde (enol).
thermometer → termometar
Thermometers are devices for measuring temperature. Linear and volume thermal expansion are macroscopic properties of matter, which can be easily measured, relative to measurements of microscopic properties, on the basis of which, temperature is defined. Thermometers based on thermal expansion are secondary instruments that is, they have to be calibrated in comparison to a standard thermometer. In a thermometer with liquid, mercury or alcohol is placed in a small glass container. If temperature increases, the liquid undergoes volume expansion and rises in a capillary. The level of the raised liquid is the measure of temperature. Mercury thermometers measure temperatures in the temperature range between -39 °C and 300 °C. Alcohol thermometers measure lower temperatures. Bimetal thermometers have a spiral spring, which consists of two metals with different coefficients of linear expansion. When temperature changes, metals undergo different change in length and the consequence twisting of the spring is transferred to a pointer, the deflection of which is the measure of temperature.
unsaturated fatty acid → nezasićena masna kiselina
Unsaturated fatty acid is a fatty acid whose carbon chain can absorb additional hydrogen atoms. Their carbon chain has one or more double or triple valence bond per molecule. The most important of these are:
| Oleic (9-octadecenoic acid) | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| Linoleic (9,12-octadecadienoic acid) | CH3(CHCH2)3(CH2CH=CH)2(CHCH2)7COOH |
| Linolenic (9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid) | CH3(CH2CH=CH)3(CHCH2)7COOH |
van’t Hoff equation → van Hoffova jednadžba
Van’t Hoff equation is the equation expressing the temperature dependence on the equilibrium constant K of a chemical reaction:
where ΔrH° is the standard enthalpy of reaction, R the molar gas constant, and T the temperature.
volumetric flask → odmjerna tikvica
Volumetric flasks are bottles made of glass, in a pear like in shape with long thin necks and flat bottoms. All come with a ground glass stopper for a tight seal. Volume marking is cut in glass with fluoride acid around the neck, so that parallax should be avoided (flask is put in front of the eyes so that one can see only a straight horizontal line). A volumetric flask is calibrated to contain (TC or In) the indicated volume of water at 20 °C when the bottom of the meniscus is adjusted to just rest on the center of the line marked on the neck of the flask. They are used for preparing the exactly known volume of sample solution and standard solutions of reagents. On each flask with volume designation a temperature on which the flask has been calibrated is designated.
water → voda
Water (H2O) (dihydrogen oxide) is a binary compound that occurs at room temperature as a clear colorless odorless tasteless liquid; freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C. Water is a chemical compound which is essential for living organisms and it is widely used as a solvent.
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Standardna vodikova elektroda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table