conditional electrode potential → uvjetni elektrodni potencijal
Conditional or formal electrode potential (E°’) is equal to electrode potential (E) when overall concentrations of oxidised and reduced form in all its forms in a solution are equal to one. Conditional electrode potential includes all effects made by reactions that do not take part in the electron exchange, but lead to change of ion power, changes of pH, hydrolysis, complexing, precipitating, etc.
At 298 K (25 °C) and by converting natural (Napierian) logarithms into decimal (common, or Briggian) logarithms, Nernst’s equation for electrode potential can be written as follows:
electrode potential → elektrodni potencijal
Electrode potential is defined as the potential of a cell consisting of the electrode in question acting as a cathode and the standard hydrogen electrode acting as an anode. Reduction always takes place at the cathode, and oxidation at the anode. According to the IUPAC convention, the term electrode potential is reserved exclusively to describe half-reactions written as reductions. The sign of the half-cell in question determines the sign of an electrode potential when it is coupled to a standard hydrogen electrode.
Electrode potential is defined by measuring the potential relative to a standard hydrogen half cell
The convention is to designate the cell so that the oxidised form is written first. For example
The e.m.f. of this cell is
By convention, at p(H2) = 101325 Pa and a(H+) = 1.00, the potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is 0.000 V at all temperatures. As a consequence of this definition, any potential developed in a galvanic cell consisting of a standard hydrogen electrode and some other electrode is attributed entirely to the other electrode
electrodeposition → elektrodepozicija
Electrodeposition is a process of depositing solid materials on an electrode surface using electrolysis. It is a somewhat loosely used term that is applied to many technologies. There are a number of metal deposition technologies. However, not only metals but also different compounds can be electrodeposited. This is used most often for the formation of oxides (such as manganese dioxide and lead dioxide) by anodic oxidation of dissolved salts.
electrodialysis → elektrodijaliza
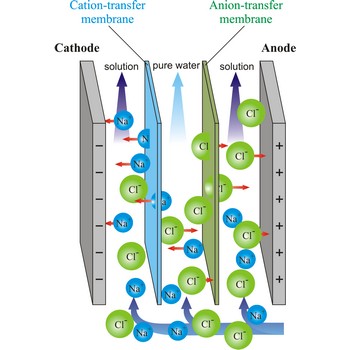
Electrodialysis is a procedure of dialysis accelerated with an electric field. Dialyser is divided into three sections. Solution flows through the middle section, between two semipermeable membranes alternately to positive ions and negative ions. An electrodes are placed in the neighbouring sections. Under the influence of electric field, positive ions will travel towards the cathode (the negative electrode), and negative ions towards the anode (the positive electrode), whereby travelling of ions through the membrane is accelerated. In this way, the feed water is separated into two streams: one of pure water and the other of more concentrated solution.
ion selective electrode → ion selektivne elektrode
Ion selective electrode (ISE) is an electrode or electrode assembly with a potential that is dependent on the concentration of an ionic species in the test solution and is used for electroanalysis. Ion-selective electrodes are often membrane type electrodes.
Nernst’s electrode potential equation → Nernstova jednadžba za elektrodni potencijal
For general reaction of some redox system
dependence of electrode potential of redox system upon activity of oxidised and reduced form in solution is described in Nernst’s equation for electrode potential:
where E = to electrode potential of redox system
E° = standard electrode potential of redox system
R = universal gas constant
T = thermodymical temperature
F = Faraday’s constant
z = number of electrons exchanged in redox reaction
aO = activity of oxidised form
aR = activity of reduced form
n = stechiometrical coefficient of oxidised form
m = stechiometrical coefficient of reduced form
sacrificial protection → zaštita žrtvovanom elektrodom
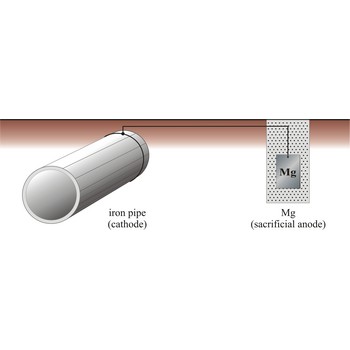
Sacrificial protection is the protection of iron or steel against corrosion by using a more reactive metal. Pieces of zinc or magnesium alloy are attached to pump bodies and pipes. The protected metal becomes the cathode and does not corrode. The anode corrodes, thereby providing the desired sacrificial protection. These items are known as sacrificial anodes and "attract" the corrosion to them rather than the iron/steel. The sacrificial anodes must be replaced periodically as they corrode.
The iron pipe will be connected to a more reactive metal such as magnesium through cooper wires, the magnesium will donate its electrons to the iron preventing it from rusting. Iron which is oxidises will immediately be reduced back to iron.
standard electrode potential → standardni elektrodni potencijal
Standard electrode potential (E°) (standard reduction potentials) are defined by measuring the potential relative to a standard hydrogen electrode using 1 mol solution at 25 °C. The convention is to designate the cell so that the oxidised form is written first. For example,
The e.m.f. of this cell is -0.76 V and the standard electrode potential of the Zn2+|Zn half cell is -0.76 V.
alpaca → alpaka
Alpaca (alpaka) or Nickel Silver is the generic name for any of a range of non-precious bright silvery-grey metal alloys, composed of copper, nickel and zinc. Despite its name it contains no real silver. It is also commonly called German Silver.
There are many different formulations of alloys which fall within the general term of Nickel Silver. All contain copper, nickel and zinc, while some formulations may additionally include antimony, tin, lead or cadmium. A representative formulation is 65 % copper, 18 % nickel, 17 % zinc. Nickel Silver is widely used for the commercial production of industrial components, housewares, flatware and cutlery, and as the metal substrate for silver-plated goods.
formaldehyde → formaldehid
Formaldehyde (methanal) is a colourless gas, HCHO; r.d. 0.815 (at -20 °C); m.p. -92 °C; b.p. -21 °C. It is the simplest aldehyde, made by the catalytic oxidation of methanol (500 °C; silver catalyst) by air. It forms two polymers: methanal trimer and polymethanal.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Srebro/srebrov klorid elektroda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table