flotation → flotacija
Flotation is a procedure in which hydrophobic solid substances are separated from hydrophilic one using bubbles of air. If air is blow through a suspension, in which substances promoting easier creation of foam are added, bubbles of air are created which stick to the hydrophobic matter and carry it out to the surface.
condensation → kondenzacija
1. Condensation is a process of changing from a gaseous to a liquid or solid state, usually done by cooling.
2. Condensation, in colloid systems, is a process where smaller particle join in one colloid size particle
3. Condensation, in chemical terms, is a sort of chemical reaction in which small molecules like water, carbon dioxide, or ammonia single out.
convection → konvekcija
Convection is the process by which heat is transferred from one part of a fluid to another by movement of the fluid itself. There are two methods by which this can be carried out.
Natural convection, in which movement occurs as a result of gravity. Heat transferred through a fluid medium, such as air or water, by currents that result from the rising of less dense, warm fluid and the sinking of heavier, cooler fluid.
Forced convection is where hot fluid is transferred from one region to another by a mechanical means (fans or pumps).
corrosion → korozija
Corrosion is a harmful and undesirable construction material consumption by the chemical activity of its surroundings. Corrosion concept refers to metal and nonmetal construction materials, but it is usually used for metals, Corrosion of metal, according to the mechanism process, is divided into chemical (corrosion in nonelectrolytes) and electrochemical (corrosion in electrolytes).
Chemical corrosion appears by direct action of molecule of some element or compound on metal, thus directly creating corrosion products.
Electrochemical corrosion of metals occurs in electrolytes, so reduction of metal atom into free cation appears which by secondary processes gives molecules of compound which are considered a corrosion product.
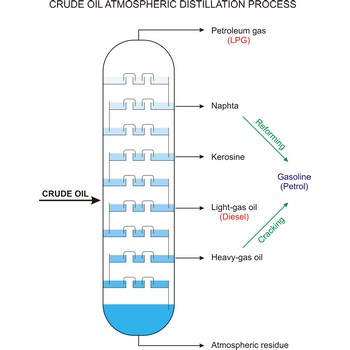
cracking → krekiranje
Cracking is the process whereby heavy molecules of petroleum or crude oil are broken down into hydrocarbons of lower molecular weight (especially in the oil-refining process).
Haber, Fritz → Haber, Fritz
Fritz Haber (1868-1934) is German physical chemist, winner of the Nobel Prize for Chemistry (1918) for his development of a method of synthesizing ammonia. With Carl Bosch, he invented a process for the large-scale production of ammonia for use in nitrogen fertilizer.
hardening → stvrdnjavanje
Hardening is the process of becoming hard or solid by cooling, or drying, or crystallization. For example, the hardening of concrete.
Helmholz free energy → Helmholzova slobodna energija
Helmholz free energy (A) is a thermodynamic function defined by A = U - TS, where U is the internal energy, S the entropy, and T the thermodynamic temperature. For a reversible isothermal process ΔA represents the useful work available.
ion exchange → ionska izmjena
Ion exchange is a process involving the adsorption of one or several ionic species accompanied by the simultaneous desorption (displacement) of one or more other ionic species.
crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Spontani proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table