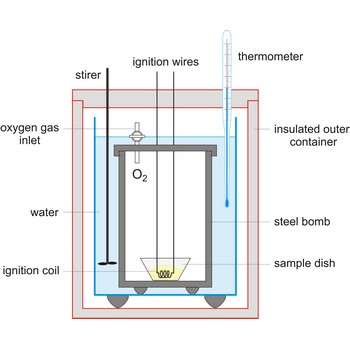
calorimeter → kalorimetar
Calorimeter is an instrument used to measure the energy absorbed or released in a chemical reaction. It also used in determining specific heat.
cellulose → celuloza
Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n, is a polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by (1→4)-β-glycoside bonds. Nature uses cellulose primarily as a structural material to impart strength and rigidity to plants. Leaves, grasses, and cotton are primarily cellulose. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc. Cellulose also serves as raw material for the manufacture of cellulose acetate, known commercially as acetate rayon, and cellulose nitrate, known as guncotton. Gunncotton is the major ingredient in smokeless powder, the explosive propellant used in artillery shells and in ammunition for firearms.
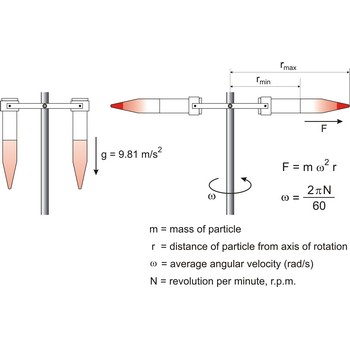
centrifuge → centrifuga
Centrifuge is a device in which solid or liquid particles of different densities are separated by rotating them in a tube in a horizontal circle. The dense particles tend to move along the length of the tube to a greater radius of rotation, displacing the lighter particles to the other end.
heat of hydration → toplina hidratacije
Heat of hydration or enthalpy of hydration of ions corresponds to the heat that is released by hydration of one mole of ions at a constant pressure. The more the ion is hydrated, the more heat is released. Degree of hydration depends on the size and charge of ion. The smaller the ion and the greater its charge, it will be the more hydrated.
heat of vaporisation → toplina isparavanja
Heat of vaporisation or enthalpy of vaporisation is the heat required to convert a substance from the liquid to the gaseous state with no temperature change (also called latent heat of vaporization).
impedance → impedancija
Impedance is the analogue of the resistance or resistivity when applied to alternating current. That is, it is a measure of a material’s inability to carry the electrical current. In many materials the impedance varies as the frequency of the applied electrical potential changes, due to the properties of the conducting liquid or solid. In electrochemistry, the impedance of the electrodes is also frequency dependent.
Knudsen number → Knudsenova značajka
Knudsen number (Kn) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where λ is mean free path and l is length.
colloid → koloid
Colloids are systems in which there are two or more phases, with one (the dispersed phase) distributed in the other (the continuous phase). Moreover, at least one of the phases has small dimensions, in the range between 1 nm and 1 μm (10-9 m – 10-6 m). Dimension, rather than the nature of the material, is characteristic. In this size range, the surface area of the particle is large with respect to its volume so that unusual phenomena occur, e.g., the particles do not settle out of the suspension by gravity and are small enough to pass through filter membranes. Macromolecules (proteins and other high polymers) are at the lower limit of this range; the upper limit is usually taken to be the point at which the particles can be resolved in an optical microscope.
Colloidal particles may be gaseous, liquid, or solid, and occur in various types of suspensions:
Sols - dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid.
Emulsions - colloidal systems in which the dispersed and continuous phases are both liquids.
Gels - colloids in which both dispersed and continuous phases have a three-dimensional network throughout the material.
Aerosols - colloidal dispersions of liquid or solid particles in a gas.
Foams - dispersions of gases in liquids or solids.
concentration → koncentracija
1. Group of four quantities characterizing the composition of a mixture with respect to the volume of the mixture (mass, amount, volume and number concentration).
2. Short form for amount (of substance) concentration (substance concentration in clinical chemistry).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Specifična veličina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table