asbestos → azbest
Asbestos is any one of a group of fibrous amphibole minerals (from the silicate group). It has widespread commercial uses because of its resistance to heat, chemical inertness., and high electrical resistance. Since 1970s short asbestos fibres have been recognized as a cause of asbestosis, a serious lung disorder, and mesothelioma, a fatal form of lung cancer. These concerns have limited its use and imposed many safety procedures when it is used.
barrier film → barijerni film
Barrier film is a thin, continuous, non-porous, electrically insulating film on metal surfaces (usually comprised of oxides).
Brownian motion → Braunovo gibanje
Brownian motion is the continuous random movement of small particles suspended in a fluid, which arise from collisions with the fluid molecules. First observed by the British botanist R. Brown (1773-1858) when studying pollen particles. The effect is also visible in particles of smoke suspended in a gas.
buffer → pufer otopina
Buffer is a solution designed to maintain a constant pH when small amounts of a strong acid or base are added. Buffers usually consist of a fairly weak acid and its salt with a strong base. Suitable concentrations are chosen so that the pH of the solution remains close to the pKa of the weak acid.
coal → ugljen
Coal is a black or brownish-black, combustible sedimentary rock, with 30 % (lignite) to 98 % (anthracite) carbon by weight, mixed with various amounts of water and small amounts of sulfur and nitrogen compounds. It is formed from plant matter that decayed in swamps and bogs that has been compressed and altered by geological processes over millions of years. Coal is primarily used as a fuel.
aspartic acid → asparaginska kiselina
Aspartic acid is an electrically charged amino acids with acidic side chains. As a group the charged amino acids are relatively abundant and are generally located on the surface of the protein. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Aspartic acid (sometimes referred to as asparate depending on pH) is non-essential in mammals, being produced from oxaloacetate by transamination.
- Abbreviations: Asp, D
- IUPAC name: 2-aminobutanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H7NO4
- Molecular weight: 133.10 g/mol
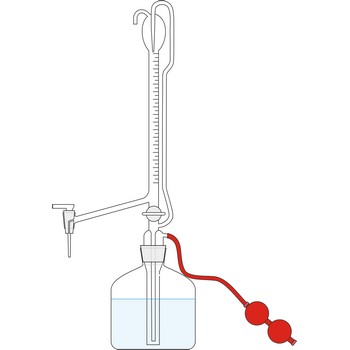
automatic burette → automatska bireta
Automatic burette is used for series of tests. It is connected with a bottle which contains the titration solution. The air is pumped into the bottle by a small rubber air pump, created the pressure in the bottle which the rises the solution to the top of burette. When the the burette is full, the valve is released, the pressure in the bottle falls and the burette automatically sets itself to zero. Work with automatic burettes is by far faster and the consumption of standard solution is smaller.
condensational polymerisation → kondenzacijska polimerizacija
Condensational polymerisation is a reaction of polymerisation in which monomers together create a polymer by losing small molecules like water.
decomposition potential → potencijal razlaganja
Decomposition potential of some system is the smallest voltage which should be applied so that electrolysis occurs.
detection limits → granica detekcije
Detection limits is the smallest quantity of analyte which it is possible to determine by means of a given technique or procedure.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Small coaxial electrical connectors." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table