complete ionic equation → potpuna ionska jednadžba
Complete ionic equation is a balanced equation that describes a reaction occurring in a solution, in which all strong electrolytes are written as dissociated ions.
decomposition potential → potencijal razlaganja
Decomposition potential of some system is the smallest voltage which should be applied so that electrolysis occurs.
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
bismuth → bizmut
Bismuth was discovered by Claude Geoffroy (France) in 1753. The origin of the name comes from the German words Weisse Masse meaning white mass; now spelled wismut and bisemutum. It is hard, brittle, steel-grey metal with a pink tint. Stable in oxygen and water. Dissolves in concentrated nitric acid. Bismuth can be found free in nature and in minerals like bismuthine (Bi2S3) and in bismuth ochre (Bi2O3) Main use is in pharmaceuticals and low melting point alloys used as fuses.
Bunsen’s cell → Bunsenov članak
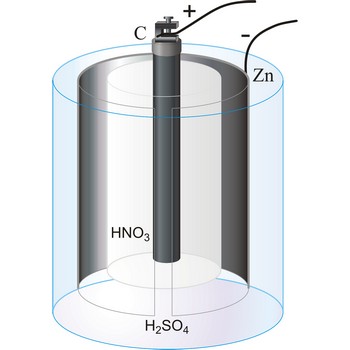
Bunsen’s cell is a primary cell devised by Robert W. Bunsen consisting of a zinc cathode immersed in dilute sulphuric acid and carbon anode immersed in concentrated nitric acid. The electrolytes are separated by a porous pot. The cell gives an e.m.f. of about 1.9 V.
diffusion current → difuzijska struja
Diffusion current (id) is a current which is limited by the speed of particle diffusion in an electrolyte solution.
electroanalytical chemistry → elektroanalitička kemija
Electroanalytical chemistry chemistry is the application of electrochemical cells and electrochemical techniques for chemical analysis. The analyte is dissolved in the electrolyte of the cell, and one can perform either qualitative analysis (determination of the type of constituents present) or quantitative analysis (determination of the amount of a given constituent).
electromotive force → elektromotorna sila
Electromotive force (e.m.f. or EMF) is the difference in electric potential that exists between two dissimilar electrodes immersed in the same electrolyte or otherwise connected by ionic conductors.
electroorganic reaction → elektroorganske reakcije
Electroorganic reaction is an organic reaction produced in an electrolytic cell. Electroorganic reactions are used to synthesise compounds that are difficult to produce by conventional techniques. An example of an electroorganic reaction is Kolbe’s method of synthesising alkanes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Slabi elektrolit." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table