thermosetting plastic → termostabilna plastika
Thermosetting plastics (thermosets) refer to a range of polymer materials that cure, through the addition of energy, to a stronger form. The energy may be in the form of heat (rubber), through a chemical reaction (two part epoxy), or irradiation. Thermoset materials are usually liquid or malleable prior to curing, and designed to be molded into their final form, or used as adhesive.
Thermoset polymer resins transformed into plastics or rubbers by cross-linking into a rigid, 3-D structure. A thermoset material cannot be melted and re-molded after it is cured.
van’t Hoff equation → van Hoffova jednadžba
Van’t Hoff equation is the equation expressing the temperature dependence on the equilibrium constant K of a chemical reaction:
where ΔrH° is the standard enthalpy of reaction, R the molar gas constant, and T the temperature.
water ion product → ionski produkt vode
Water ion product (Kw) is a concentration product of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. For the reaction:
the equilibrium expression would be:
Note that all pure liquid terms are omitted, hence H2O does not appear in the denominator. At 25 °C, Kw = 1.0×10-14 mol2dm-6 = (Ka)(Kb)
Winkler’s method → Winklerova metoda
Winkler’s method was once a common method used to determine the dissolved oxygen concentration by titration. Now rarely used due to the accuracy and low price of oxygen meters.
The water sample is first treated with excess manganese(II) sulfate solution and then with an alkaline solution of potassium iodide. The Mn(OH)2 initially formed reacts with the dissolved oxygen. The amount of MnO(OH)2 formed is determined by reaction with iodide ion in acidic solution. The iodine formed may be titrated against standard thiosulfate solution, using starch as an indicator.
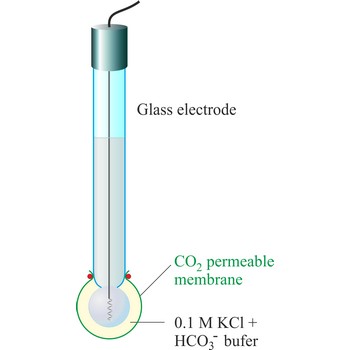
CO2 ion selective electrode → CO2 ion selektivna elektroda
The carbon dioxide ion selective electrode uses a gas-permeable membrane to separate the sample solution from the electrode internal solution. Dissolved carbon dioxide in the sample solution diffuses through the membrane until an equilibrium is reached between the partial pressure of CO2 in the sample solution and the CO2 in the internal filling solution. In any given sample the partial pressure of carbon dioxide will be proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide. The diffusion across the membrane affects the level of hydrogen ions in the internal filling solution:
The hydrogen level of the internal filling solution is measured by the pH electrode located behind the membrane. The internal filling solution contains a high concentration of sodium bicarbonate (e.g. 0.1 mol/L NaHCO3) so that the bicarbonate level can be considered constant.
Lennard-Jones potential → Lennard-Jonesov potencijal
The Lennard-Jones potential (or 12-6 potential) is a mathematically simple model that describes the interaction between two non-bonded and uncharged atoms (known as the van der Waals interaction). It was first proposed in 1924 by British physicist Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones (1894-1954). The Lennard-Jones Potential is given by the following equation
V(r) = 4e[(sigma/r)12-(sigma/r)6)]
where V is the intermolecular potential between the two atoms or molecules, ε is the well depth and a measure of how strongly the two particles attract each other, σ is the distance at which the intermolecular potential between the two particles is zero, r is the distance of separation between centres of both particles.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Reverzibilna reakcija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table