methyl orange → metil oranž
Methyl orange is an acid-base indicator, in acid it turns red and in a base it turns yellow.
Nernst’s electrode potential equation → Nernstova jednadžba za elektrodni potencijal
For general reaction of some redox system
dependence of electrode potential of redox system upon activity of oxidised and reduced form in solution is described in Nernst’s equation for electrode potential:
where E = to electrode potential of redox system
E° = standard electrode potential of redox system
R = universal gas constant
T = thermodymical temperature
F = Faraday’s constant
z = number of electrons exchanged in redox reaction
aO = activity of oxidised form
aR = activity of reduced form
n = stechiometrical coefficient of oxidised form
m = stechiometrical coefficient of reduced form
galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
Knudsen burette → Knudsenova bireta
Knudsen's automatic bulb-burette, developed by the Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949), is designed in a way that even routine field analysis in a boat laboratory would provide highly accurate measurements. The burette is filled with a mixture of silver nitrate from reservoir R, located above the burette, by opening the A valve. When the solution crosses the three-way C valve the A valve is closed preventing further solution flow in to the burette. Any extra solution is caught in the W bowl. Turn the C valve, which marks the zero on the scale, in order to allow atmospheric air to enter the burette. Since most open-ocean samples lie in a relatively small chlorinity range, the burette is designed so that much of its capacity is in the bulb (B). This allows the titration to be quick (by quickly releasing contents from the B area) and reduces the error that occurs from the slow drainage along the inner wall of the burette.
Each millimeter is divided in to twenty parts (double millimeter division of the Knudsen burette) which allows for highly accurate measurements (the scale is read up to a precision of 0.005 mL). From 0 to 16 the burette isn't divided, that usually starts from 16 and goes until 20.5 or 21.5. A single double millimeter on a Knudsen burette scale corresponds to one permille of chloride in the seawater sample. This burette can be used for titration of water from all of the oceans and seas, with the exemptions being areas with very low salinity (e.g. the Baltic Sea) and river estuaries which require the use of normal burettes.
standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
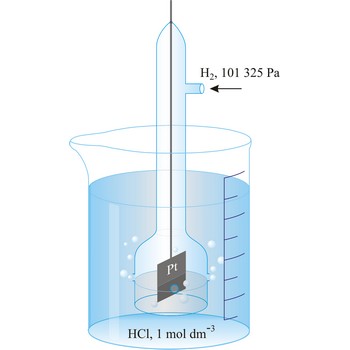
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
Winkler’s method → Winklerova metoda
Winkler’s method was once a common method used to determine the dissolved oxygen concentration by titration. Now rarely used due to the accuracy and low price of oxygen meters.
The water sample is first treated with excess manganese(II) sulfate solution and then with an alkaline solution of potassium iodide. The Mn(OH)2 initially formed reacts with the dissolved oxygen. The amount of MnO(OH)2 formed is determined by reaction with iodide ion in acidic solution. The iodine formed may be titrated against standard thiosulfate solution, using starch as an indicator.
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Redoks-titracija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table