oxidating agent → oksidans
Oxidating agent is a substance that receives electrons and oxidates other substances. Oxidating agent is always reduced in this reaction.
oxidation → oksidacija
The term oxidation originally meant a reaction in which oxygen combines chemically with another substance. More generally, oxidation is a part of a chemical reaction in which a reactant loses electrons (increases oxidation number). Simultaneous reduction of a different reactant must occur (redox reaction).
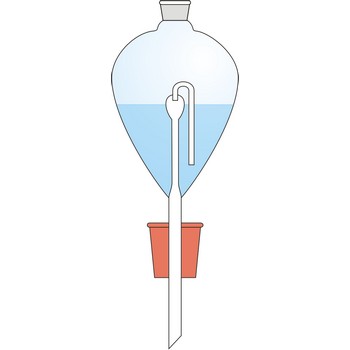
Contat-Gockel’s valve → Contat-Gockelov ventil
Contat-Göckel’s valve is used for maintenance of inert atmosphere in a flask. The valve is filled with a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) so that the end of the tube is covered. Solution inside the valve keeps the flask contents away from the oxygen influence from air. If low pressure is created inside the flask (when the flask is cooled), the solution will penetrate inside it from funnel and in a reaction with acid CO2 is generated which fills up the flask.
Solution from the funnel will keep penetrating until CO2 pressure in the flask is equalised with the outer pressure.
copolymer → kopolimer
Copolymers are also known as heteropolymers. They are made from two (or more) different monomers, which usually undergo a condensation reaction with the elimination of a simple molecule, such as ammonia or water. A typical example is the condensation of 1,6-diaminohexane (hexamethylenediamine) with hexanedioic acid (adipic acid) to form nylon 6,6.
The properties of a polymeric plastic can most easily be modified if it is a copolymer of two or more different monomers, e.g. acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS). Varying the proportions of the component monomers can preselect its properties.
cyclic voltammetry → ciklička voltametrija
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is an electrochemical measuring technique used for the determination of the kinetics and mechanism of electrode reactions. The potential of the working electrode is controlled (typically with a potentiostat) and the current flowing through the electrode is measured. It is a linear-weep voltammetry with the scan continued in the reverse direction at the end of the first scan. This cycle can be repeated a number of times, and is used for corrosion studies.
Dalton’s atomic theory → Daltonova atomska teorija
Dalton’s atomic theory is a theory of chemical combination, first stated by John Dalton in 1803. It involves the following postulates:
1. Elements consist of indivisible small particles (atoms).
2. All atoms of the same element are identical; different elements have different types of atom.
3. Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
4. ’Compound elements’ (i.e. compounds) are formed when atoms of different elements join in simple ratios to form ’compound atoms’ (i.e. molecules).
Dalton also proposed symbols for atoms of different elements (later replaced by the present notation using letters).
polycondensational polymer → polikondenzacijski polimer
Polycondensational polymers are compounds which are obtained by condensation polymerization with successive repetitions of the condensation reaction.
precipitate → precipitat
Precipitate or the deposit is an insoluble solid formed by reactions in a solution. For example, when a solution of silver nitrate is added to a solution of sodium chloride, insoluble silver chloride precipitates.
racemisation → racemizacija
Racemisation is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into an optically inactive form which half of the optically active substance becomes its miror image (enantiomer).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Reakcije adicije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table