glass → staklo
Glass is a brittle transparent solid with the molecular structure of a liquid. It is made by fusing together sand (SiO2), soda (Na2CO3), and lime (CaCO3) with small quantities other compounds. It is used for window panes and mirrors, for articles of table and culinary use, for lenses, and various articles of ornament.
Heat of atomisation → toplina atomiziranja
Heat of atomisation or enthalpy of atomisation is the energy required to dissociate one mole of a given substance into atoms.
heat of combustion → toplina izgaranja
Heat of combustion or enthalpy of combustion is the heat evolved when a definite quantity of a substance is completely oxidised (burned).
heat of crystallization → toplina kristalizacije
Heat of crystallization or enthalpy of crystallization is the heat evolved or absorbed when one mole of given substance crystallises from a saturated solution of the same substance.
extraction → ekstrakcija
Extraction is the separation of a component from its mixture by selective solubility. When a solution of one substance in one solvent is brought in with another solvent dissolved substance will distribute between the two solutants because of different solubility. Extraction is an efficient and fast method used for separating and concentrating matters. Extraction is best done several times in a succession, with smaller amount of solvent in it the matter is better dissolved. For example, caffeine can be separated from coffee beans by washing the beans with supercritical fluid carbon dioxide; the caffeine dissolves in the carbon dioxide, but flavour compounds do not. Vanillin can be extracted from vanilla beans by shaking the beans with an organic solvent, like ethanol.
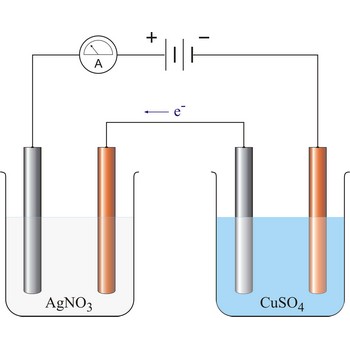
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis → Faradayevi zakoni elektrolize
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are two laws found by British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) in his experiments on electrolysis:
1. The quantity of matter extracted on the electrode is proportional to the quantity of charge (Q = I·t) which has flown in electrolysis time.
where z = number of electrons changed in reaction and F = Faraday’s constant which equals 96 487 C mol-1.
2. The masses of the elements liberated by the same quantity of electricity are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
96 487 C will discharge 1 mol Ag and 1/2 mol Cu. The relevant half reactions are:
heat of formation → toplina nastajanja
Heat of formation or enthalpy of is formation the heat evolved or absorbed when one mole of a compound is formed in its standard state from its constituent elements.
heat of fusion → toplina taljenja
Heat of fusion or enthalpy of fusion is the heat required to convert a substance from the solid to the liquid state with no temperature change (also called latent heat of fusion or melting).
heat of reaction → toplina kemijske reakcije
Heat of reaction or enthalpy of reaction is the heat evolved or absorbed as a result of the complete chemical reaction of molar amounts of the reactants.
heat of sublimation → toplina sublimacije
Heat of sublimation or enthalpy of sublimation is the energy required to convert one mole of a substance from the solid to the gas state (sublimation) without the appearance of the liquid state.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Rasprostranjenost tvari." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table