abundance of substances → rasprostranjenost tvari
Abundance of substances is the ratio of the total mass of a specified element in the Earth’s crust to the total mass of the Earth’s crust. It is often expressed as a percentage.
abundance of elements → rasprostranjenost elemenata
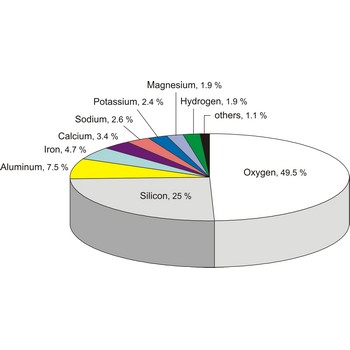
Elements in nature are mostly found in different compounds and, rarely, in the free (elementary) state. In Earth’s crust the most abundant of all elements is oxygen (with 49.5 %), then silicon (25 %), aluminium (7.5 %), iron (4.7 %), calcium (3.4 %), sodium (2.6 %), potassium (2.4 %), magnesium (1.9 %) and hydrogen (1.9 %). These nine elements make up almost 99 % of the Earth’s composition.
carcinogen → kancerogene tvari
Carcinogen is any substance that can cause or contribute to the production of cancer.
amphoteric substances → amfoterna tvar
Amphoteric substances can behave as acids or as bases depending upon their surroundings. So aluminium hydroxide in reaction with acids will behave as a base
and in reaction with bases it will act as an acid
dissolved substance → otopljena tvar
Dissolved substance is a solid, liquid or gas matter dissolved in a solvent. Depending upon the particle size of dissolved substance, solutions differ in properties and can be divided into real solutions (diameter of particles is smaller than 1 nm), colloid solutions (diameter of particles is from 1 nm to 200 nm) and suspensions (diameter of particles is greater than 200 nm).
elementary substance → elementarna tvar
Elementary substance is a simple and pure substance which can not be, by chemistry methods, decomposed further into simpler substances.
foreign matter → strana tvar
Foreign matter most commonly refers to the presence of unwanted or undesirable material present in foods or chemicals.
impure substance → nečista tvar
Impure substance is every substance that contains traces of other elements or compounds in itself.
insoluble substance → netopljiva tvar
Insoluble substance is a substance that does not dissolve in a solvent to give a reasonable concentration (e.g. chalk is insoluble in water).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Rasprostranjenost tvari." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table