square pyramidal molecular geometry → kvadratna piramidalna geometrija molekule
Square pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are five bonds and one lone pair on the central atom in the molecule. Bromine pentafluoride (BrF5) has the geometry of a square pyramid, with fluorine atoms occupying five vertices, one of which is above the plane of the other four. This molecule is made up of six equally spaced sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybrid orbitals arranged at 90° angles. The shape of the orbitals is octahedral. Because of the high symmetry of the octahedral arrangement, all six positions are equivalent, so it does not matter in which position in the drawing we put the lone pair. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
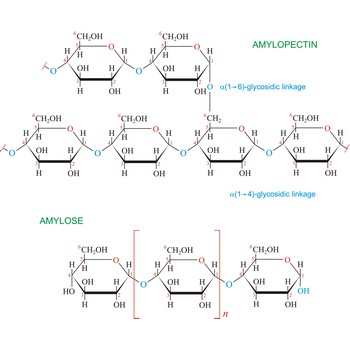
starch → škrob
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
thermite → termit
Thermite is a stoichiometric powdered mixture of iron(II) oxide and aluminium for the reaction
The reaction is highly exothermic and the increase in temperature (over 2500 °C) is sufficient to melt the iron produced. It has been used for localized welding of steel object (e.g. railway lines) in the thermit process. Thermite is also used in incendiary bombs.
thin layer chromatography → tankoslojna kromatografija
Thin layer chromatography. (TLC) is a technique for separating components in a mixture on the basis of their differing polarities. A spot of sample is placed on a flat sheet coated with silica and then carried along by a solvent that soaks the sheet. Different components will move different distances over the surface. TLC is a useful screening technique in clinical chemistry; for example, it can be used to detect the presence of drugs in urine.
transition metal → prijelazni element
This group of metals is distinguished from other metals not by their physical properties, but by their electronic structure. Transition metals are elements characterized by a partially filled d subshell. The First Transition Series comprises scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu). The Second and Third Transition Series include the lanthanides and actinides, respectively.
The transition metals are noted for their variability in oxidation state. Thus, manganese has two electrons in its outside shell and five electrons in the next shell down, and exhibits oxidation states of +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, and +7.
They are also characterised by the fact that well into the series, going from left to right, the properties of the succeeding metals do not differ greatly from the preceding ones.
tyrosine → tirozin
Tyrosine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tyrosine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tyrosine has special properties since its hydroxyl side chain may function as a powerful nucleophile in an enzyme active site (when ionized) and is a common site for phosphorylation in cell signaling cascades. Tyrosine absorbs ultraviolet radiation and contributes to the absorbance spectra of proteins. It is not essential (or semi-essential) to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites.
- Abbreviations: Tyr, Y
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO3
- Molecular weight: 181.19 g/mol
visible radiation → vidljivo zračenje
Human eye can only see electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths form 400 nm to 760 nm. This narrow part of electromagnetic spectrum is called visible radiation. Visible (white) light is a mixture of light of all kind of colours, it can be separated, with the help of a glass prism, into its component colours - visible light spectrum, and each colour corresponds to a certain area of wavelengths:
| Colour | Wavelength / nm |
|---|---|
| purple | 400 - 450 |
| blue | 450 - 500 |
| green | 500 - 570 |
| yellow | 570 - 590 |
| orange | 590 - 620 |
| red | 620 - 760 |
X-ray diffraction → rendgenska difrakcija
The regular array of atoms in a crystal is a three-dimensional diffraction grating for short-wavelength waves such as X-rays. The atoms are arranged in planes with interplanar spacing d. Diffraction maxima occur in the incident direction of the wave, measured from the surface of a plane of atoms, and the wavelength λ of the radiation satisfy Braggs’s law:
yttrium → itrij
Yttrium was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1843. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is silvery, ductile, fairly reactive metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Easily combustible, reacts with oxygen in water to release hydrogen. Yttrium is found in minerals such as monazite, xenotime and yttria. Combined with europium to make red phosphors for colour TV’s. Yttrium oxide and iron oxide combine to form a crystal garnet used in radar.
zeolite → zeolit
Zeolite is a natural or synthetic hydrated aluminosilicate with an open three-dimensional crystal structure, in which water molecules are held in cavites in the latice. The water can be driven off by heating and the zeolite can then absorb other molecules of suitable size. Zeolites are used for separating mixtures by selective absorption.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Racematna smjesa." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table