composition of ocean water → sastav oceanske vode
The proportions of the major constituents of ocean water are almost constant throughout the world. Salinity (total salt content) and the concentrations of individual chemical constituents in sea wateris given the units psu (practical salinity units). For most purposes one can assume that the new unit, psu, and the older unit, ‰, are synonymous.
The average composition of the ocean water is as shown on the following table.
| Constituent | Percentage of total salt |
|---|---|
| Chlorine | 55.3 % |
| Sodium | 30.8 % |
| Magnesium | 3.7 % |
| Sulphur | 2.6 % |
| Calcium | 1.2 % |
| Potassium | 1.1 % |
condensation → kondenzacija
1. Condensation is a process of changing from a gaseous to a liquid or solid state, usually done by cooling.
2. Condensation, in colloid systems, is a process where smaller particle join in one colloid size particle
3. Condensation, in chemical terms, is a sort of chemical reaction in which small molecules like water, carbon dioxide, or ammonia single out.
conditional electrode potential → uvjetni elektrodni potencijal
Conditional or formal electrode potential (E°’) is equal to electrode potential (E) when overall concentrations of oxidised and reduced form in all its forms in a solution are equal to one. Conditional electrode potential includes all effects made by reactions that do not take part in the electron exchange, but lead to change of ion power, changes of pH, hydrolysis, complexing, precipitating, etc.
At 298 K (25 °C) and by converting natural (Napierian) logarithms into decimal (common, or Briggian) logarithms, Nernst’s equation for electrode potential can be written as follows:
convection → konvekcija
Convection is the process by which heat is transferred from one part of a fluid to another by movement of the fluid itself. There are two methods by which this can be carried out.
Natural convection, in which movement occurs as a result of gravity. Heat transferred through a fluid medium, such as air or water, by currents that result from the rising of less dense, warm fluid and the sinking of heavier, cooler fluid.
Forced convection is where hot fluid is transferred from one region to another by a mechanical means (fans or pumps).
covalent compound → kovalentni spoj
Covalent compound is a compound made of molecules - not ions, such as H2O, CH4, Cl2. The atoms in the compound are bound together by shared electrons. Also called a molecular compound.
critical point → kritična točka
In general, critical point is the point on the phase diagram of a two-phase system at which the two coexisting phases have identical properties and therefore represent a single phase. At the liquid-gas critical point of a pure substance, the distinction between liquid and gas vanishes, and the vapour pressure curve ends. The coordinates of this point are called the critical temperature and critical pressure. Above the critical temperature it is not possible to liquefy the substance.
critical temperature → kritična temperatura
Critical temperature is the temperature of the liquid-vapour critical point, that is, the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied by an increase of pressure.
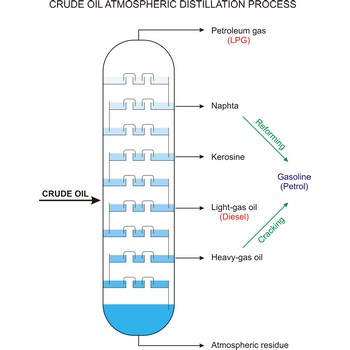
crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
dissolved substance → otopljena tvar
Dissolved substance is a solid, liquid or gas matter dissolved in a solvent. Depending upon the particle size of dissolved substance, solutions differ in properties and can be divided into real solutions (diameter of particles is smaller than 1 nm), colloid solutions (diameter of particles is from 1 nm to 200 nm) and suspensions (diameter of particles is greater than 200 nm).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Prirodni plin." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table