Chitosan → Kitozan
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed N-acetyl D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine units. It can be easily derived from partial deacetylation of natural polymer chitin. At a minimum deacetylization level of 60 % (amount of free amino groups in the polymer) it is considered to be chitosan. Thanks to the amino groups of D-glucosamine, chitosan can be protonated and turned into polycation, which is one of the sources of unique properties of chitosan as biopolymer, like aqueous solubility, antibacterial properties, biodegradability with non-toxic residues and biocompatibility.
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
Dipeptide → Dipeptid
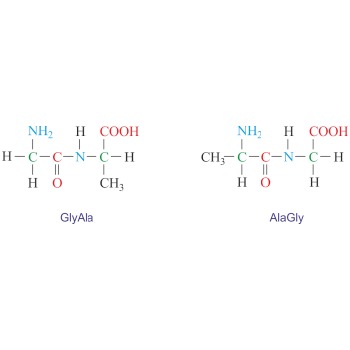
Dipeptide is an organic compound formed when two amino acids are joined by a peptide bond. Depending on which groups of amino acids are involved in the peptide bond four dipeptides can be formed from two different amino acids. For example, glycine (Gly) and alanine (Ala) can give two symmetrical dipeptides (GlyGly and AlaAla) and two unsymmetrical dipeptides (GlyAla and AlaGly). The naming is done by reading the sequence from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Primarni amin." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table