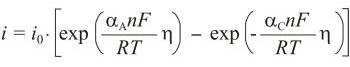brass → mjed
Brasses are alloys of copper and zinc (generally 5 % to 40 %). Brass has been known to man since prehistoric times, long before zinc itself was discovered. It was produced by melting copper together with calamine, a zinc ore. Its ductility reaches a maximum with about 30 % zinc and its tensile strength with 45 % although this property varies greatly with the mechanical and heat treatment of the alloy. Typical applications included gears, plumbing ware fittings, adapters, valves and screw machine products. The French horn is a valved brass wind instrument.
Brass may contain small amounts of other alloying elements, such as aluminum, lead, tin, or nickel. Lead can be added as an alloying element resulting in a brass that can be rapidly machined and produces minimal tool wear. Additions of aluminium, iron and manganese to brass improve strength, whilst silicon additions improve wear resistance. Brass containing tin (< 2 % ) is less liable to corrosion in seawater; it is sometimes called naval brass and is used in naval construction.

Bunsen burner → Bunsenov plamenik
Bunsen burner is a standard source of heat in the laboratory. German chemist Roberts Bunsen (1811-1899) improved the burner's design, which had been invented by Faraday, to aid his endeavors in spectroscopy. The Bunsen burner has a vertical metal tube through which a fine jet of fuel gas is directed. Air is drawn in through airholes near the base of the tube and the mixture is ignited and burns at the tube’s upper opening. The flow of this air is controlled by an adjustable collar on the side of the metal tube. When the whole is closed a yellow safety flame is displayed. Where as when the whole is open it displays a power dull blue flame with a faint blue outer flame with a vibrant blue core used u for combustion and hearting. The flame can reach temperatures of 1 500 °C.
Butler-Volmer equation → Butler-Volmerova jednadžba
Butler-Volmer equation is an activation controlled reaction, the one for which the rate of reaction is controlled solely by the rate of the electrochemical charge transfer process, which is in turn an activation-controlled process. This gives rise to kinetics that are described by the Butler-Volmer equation:
where io is exchange current density, η is overpotential (η = E - Eo), n is number of electrons, αA is anodic transfer coefficient, and αC is cathodic transfer coefficient
enthalpy growth → prirast entalpije
Enthalpy growth (ΔH) is that part of energy of system which can be translated into heat (Q) with a permanent pressure.
explosion → eksplozija
Explosion is a rapid violent chemical reaction that produces large amounts of gas and heat, accompanied by light, sound and a high-pressure shock wave.
Faradaic reaction → Faradejska reakcija
Faradaic reaction is a heterogeneous charge-transfer reaction occurring at the surface of an electrode.
calorimeter → kalorimetar
Calorimeter is an instrument used to measure the energy absorbed or released in a chemical reaction. It also used in determining specific heat.
Carnot cycle → Carnotov kružni proces
Carnot cycle is the most efficient cycle of operations for a reversible heat engine. Published in 1824 by French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), it consists of four operations on the working substance in the engine:
1-2: Isothermal expansion at thermodynamic temperature T1 with heat QH taken in.
2-3: Adiabatic expansion with a fall of temperature to T2.
3-4: Isothermal compression at temperature T2 with heat QC given out.
4-1: Adiabatic compression at temperature back to T1.
According to the Carnot principle, the efficiency of any reversible heat engine depends only on the temperature range through which it works, rather than the properties of the working substances.
coenzyme a → koenzim a
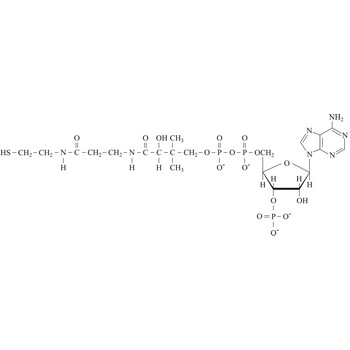
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential metabolic cofactor synthesized from cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and ATP. CoA plays important roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. One of the main functions of CoA is the carrying and transfer of acyl groups. Acylated derivatives (acetyl-CoA) are critical intermediates in many metabolic reactions.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Prijenos topline." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table