Celsius → Celzijev stupanj
Celsius (°C) is a common but non-SI unit of temperature, defined by assigning temperatures of 0 °C and 100 °C to the freezing and boiling points of water, respectively.
binary solution → binarna otopina
Binary solution is a mixture of two liquids that are completely miscible one with another. The boiling point of binary solution depends upon the solution composition and there can be three cases:
1. the boiling points of solutions of all compositions lie between the boiling points of clean liquids
2. the boiling points of solutions of any composition lie above the boiling points of clean liquids
3. the boiling points of solutions of some compositions lie below the boiling points of clean liquids
Celsius temperature scale → Celsiusova temperaturna skala
For value of zero in Celsius temperature scale the freezing point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken as another reference point. This range is divided into 100 equal parts, and each part is an equivalent to 1 °C. Units of Celsius temperature scale (°C) and thermodynamic temperature scale (K) are identical
1 °C = 1 K.
collision theory → teorija sudara
Collision theory is theory that explains how chemical reactions take place and why rates of reaction alter. For a reaction to occur the reactant particles must collide. Only a certain fraction of the total collisions cause chemical change; these are called successful collisions. The successful collisions have sufficient energy (activation energy) at the moment of impact to break the existing bonds and form new bonds, resulting in the products of the reaction. Increasing the concentration of the reactants and raising the temperature bring about more collisions and therefore more successful collisions, increasing the rate of reaction.
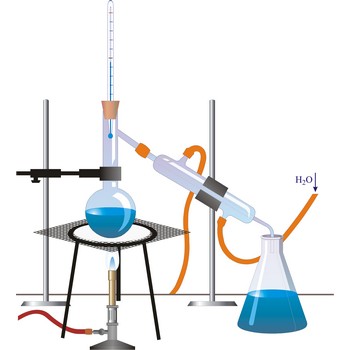
distillation → destilacija
Distillation is a process of boiling a liquid and condensing and collecting the vapour. The liquid collected is the distillate. The usual purpose of distillation is purification or separation of the components of a mixture. This is possible because the composition of the vapour is usually different from that of liquid mixture from which it is obtained. Petrol, kerosene, fuel oil, and lubricating oil are produced from petroleum by distillation.
evaporation → isparavanje
Evaporation is the change of state of a liquid into a vapour at a temperature below the boiling point of the liquid.
heat of vaporisation → toplina isparavanja
Heat of vaporisation or enthalpy of vaporisation is the heat required to convert a substance from the liquid to the gaseous state with no temperature change (also called latent heat of vaporization).
Fahrenheit scale → Fahrenheitova skala
Fahrenheit scale is the temperature scale in which 212 degrees is the boiling point of water and 32 degrees is the freezing point of water. The scale was invented in 1714 by the German physicist G.D. Fahrenheit (1686-1736).
32 °F = 0 °C
212 °F = 100 °C
1 °F =(5/9) °C
T(°C) = (5/9)[T(°F) - 32]
T(°F) = (9/5)T(°C) + 32
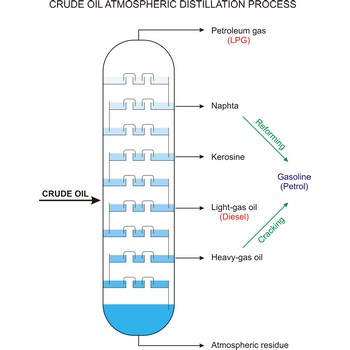
fractional distillation → frakcijska destilacija
Fractional distillation is a procedure in which liquids of close boiling points are separated. It is conducted in fraction or rectification columns in a way that vapour phase created by distillation is condensed and the condensate thus obtained is redistilled. The procedure is repeated several times. Vapour phase always contains more volatile component than the liquid phase, at top of the column vapour of clean volatile component gets out and at the bottom of the column liquid of nonvolatile component.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Povišenje vrelišta." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table