chemical symbols → kemijski simboli
Chemical symbols are a derived way of showing elements in a formula or equation. Each symbol represents one atom and it usually consists of the first two letters of the Greek or Latin name of the element.
aspartic acid → asparaginska kiselina
Aspartic acid is an electrically charged amino acids with acidic side chains. As a group the charged amino acids are relatively abundant and are generally located on the surface of the protein. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Aspartic acid (sometimes referred to as asparate depending on pH) is non-essential in mammals, being produced from oxaloacetate by transamination.
- Abbreviations: Asp, D
- IUPAC name: 2-aminobutanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H7NO4
- Molecular weight: 133.10 g/mol
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
elementary reaction → elementarna reakcija
Elementary reaction is a reaction that occurs in a single step. Equations for elementary reactions show the actual molecules, atoms, and ions that react on a molecular level.
binary solution → binarna otopina
Binary solution is a mixture of two liquids that are completely miscible one with another. The boiling point of binary solution depends upon the solution composition and there can be three cases:
1. the boiling points of solutions of all compositions lie between the boiling points of clean liquids
2. the boiling points of solutions of any composition lie above the boiling points of clean liquids
3. the boiling points of solutions of some compositions lie below the boiling points of clean liquids
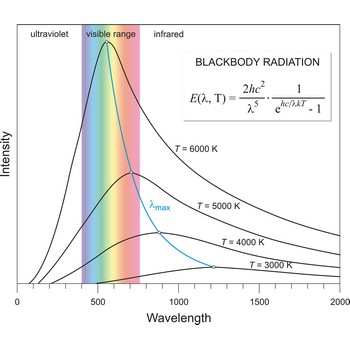
blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
equivalent weight → ekvivalentna masa
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in a neutralization reaction is that mass of substance (molecule, ion, or paired ion) that either reacts with or supplies 1 mol of hydrogen ions in that reaction.
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in an oxidation/reduction reaction is that weight which directly or indirectly produces or consumes 1 mol of electrons.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Potpuna ionska jednadžba." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table