thermal expansion → toplinsko rastezanje
Thermal expansion is a change in dimensions of a material resulting from a change in temperature. All objects change size with changes in temperature. The change ΔL in any linear dimension L is given by
in which α is the thermal coefficient of linear expansion, Lo is the initial or reference dimension at temperature To (reference temperature) and ΔT is change in temperature which causes the change in dimension.
The change ΔV in the volume of a sample of solid or liquid is
Here γ is coefficient of volume expansion, Vo is the volume of the sample at temperature To and ΔV is the change in volume over the temperature range ΔT. With isotropic substances, the coefficient of volume expansion can be calculated from the coefficient of linear expansion: γ = 3α.
thermometer → termometar
Thermometers are devices for measuring temperature. Linear and volume thermal expansion are macroscopic properties of matter, which can be easily measured, relative to measurements of microscopic properties, on the basis of which, temperature is defined. Thermometers based on thermal expansion are secondary instruments that is, they have to be calibrated in comparison to a standard thermometer. In a thermometer with liquid, mercury or alcohol is placed in a small glass container. If temperature increases, the liquid undergoes volume expansion and rises in a capillary. The level of the raised liquid is the measure of temperature. Mercury thermometers measure temperatures in the temperature range between -39 °C and 300 °C. Alcohol thermometers measure lower temperatures. Bimetal thermometers have a spiral spring, which consists of two metals with different coefficients of linear expansion. When temperature changes, metals undergo different change in length and the consequence twisting of the spring is transferred to a pointer, the deflection of which is the measure of temperature.
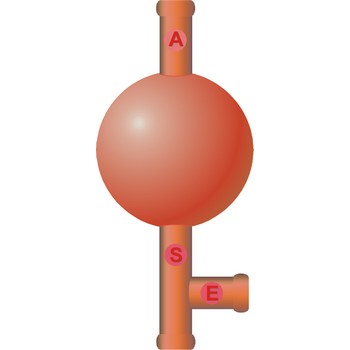
three way safety bulb → propipeta
Three way safety bulb (pipette filler bulb) is used for pipeting. The attachment is placed over the mouth of the pipet. Squeeze the air valve (A) and the bulb simultaneously to empty the bulb of air. Place the tip of the pipet below the solution's surface in the beaker. Gradually squeeze the suction valve (S) to draw liquid into the pipet. If the level of the solution is not high enough, squeeze the air valve (A) and the bulb again to expel the air from the bulb. Draw up more liquid by squeezing the suction valve (S). When the liquid is above the specified volume, stop squeezing the suction valve (S). Do not remove the bulb from the pipet. Do not allow liquid to enter the pipet bulb.
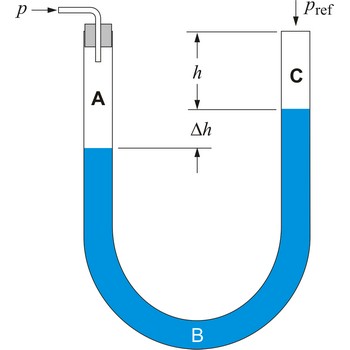
U-tube manometer → U-manometar
U-tube manometer contains water or mercury in a U-shaped tube, and is usually used to measure gas pressure. One end of the U tube is exposed to the unknown pressure field (P) and the other end is connected to a reference pressure source (usually atmospheric pressure) (Pref), shown in the schematic below.
If fluid C is the atmosphere, fluid B is the liquid in the U tube (e.g. water or mercury), and fluid A is a gas, then we can assume that ρB >> ρA, ρC. The pressure contributed by the weight of gas within the U tube can therefore be neglected. The gage pressure of the gas can be approximated by,
unsaturated fat → nezasićena mast
Unsaturated fats, which include one or more unsaturated fatty acid, are liquid at room temperature (oil) and come from plant oils such as olive, peanut, corn, sunflower, safflower, and soybean. The fish oils may also be high in unsaturated fatty acids.
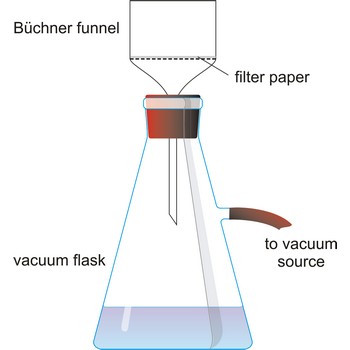
vacuum filtration → vakuum filtracija
Vacuum filtration is a technique for separating a solid product from a liquid. The mixture of solid and liquid is poured through a filter paper in a Buchner funnel. The solid is trapped by the filter and the liquid is drawn through the funnel into the flask below, by a vacuum.
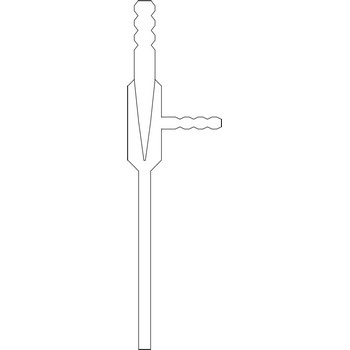
volumetric pipette → prijenosna pipeta
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette.
water → voda
Water (H2O) (dihydrogen oxide) is a binary compound that occurs at room temperature as a clear colorless odorless tasteless liquid; freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C. Water is a chemical compound which is essential for living organisms and it is widely used as a solvent.
water jet vacuum pump → vodena sisaljka
The water jet vacuum pump or vacuum aspirator is one of the most popular devices that produces vacuum in laboratories. The rapid flow of water through the device creates a vacuum in a side-arm that is connected to a vacuum application such a Buchner flask. The water jet vacuum pump creates a vacuum by means of Venturi effect named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822). The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. Water jet pumps are manufactured of glass, plastic or metal, depending on the conditions in which they are used.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Pothlađena tekućina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table