valence bond theory → teorija valentne veze
Valence bond theory is a theory that explains the shapes of molecules in terms of overlaps between half-filled atomic orbitals, or half filled hybridised orbitals.
asparagine → asparagin
Asparagine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. The polar amino acids are an important class of amino acids since they provide many of the functional groups found in proteins. Asparagine is a common site for attachment of carbohydrates in glycoproteins. In general this is not very reactive residues. Asparagine is amide derivative of aspartic acid. Asparagine is not essential for humans, which means that it can be synthesized from central metabolic pathway intermediates and is not required in the diet.
- Abbreviations: Asn, N
- IUPAC name: 2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H8N2O3
- Molecular weight: 132.12 g/mol
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
Lewis, Gilbert N. → Lewis, Gilbert N.
Gilbert Newton Lewis (1875-1946) is an American chemist whose theory of the electron pair fostered understanding of the covalent bond and extended the concept of acids and bases.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
organometallic compound → organometalni spoj
Organometallic compounds are compounds in which there is a covalent connection between atoms of carbons and atoms of metal (C-Me).
Pauling scale → Paulingova skala
Pauling scale is a numerical scale of electronegativities based on bond-energy calculations for different elements joined by covalent bonds. Electronegativity is the power of an atom when in a molecule to attract eletrons to itself. Fluorine is the most electronegative element with a Pauling electronegativity value of 4.
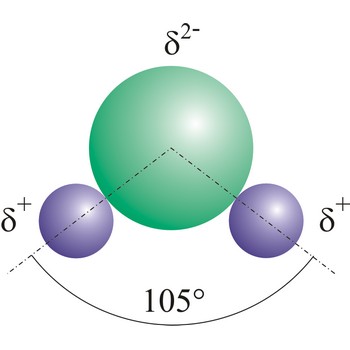
dipole molecule → dipolna molekula
Dipole molecules are created when mutual electronic pair at covalent bond is asymmetrical. If different atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, which can have different electron affinity, then the the atom with greater electron affinity will attract the electron pairs more strongly. In this way an asymmetrical distribution of negative charge appears in a molecule, so one part of the molecule becomes relatively negatively (the one closer to the electron pair) and the other becomes relatively positively charged.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Polarna kovalentna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table