non-water solution → nevodena otopina
Non-water solution is a solution in which the solvent is not a water (usualy non-polar).
organic solvent → organsko otapalo
Organic solvent is an organic liquid in which organic (non-polar) substances melt.
critical point → kritična točka
In general, critical point is the point on the phase diagram of a two-phase system at which the two coexisting phases have identical properties and therefore represent a single phase. At the liquid-gas critical point of a pure substance, the distinction between liquid and gas vanishes, and the vapour pressure curve ends. The coordinates of this point are called the critical temperature and critical pressure. Above the critical temperature it is not possible to liquefy the substance.
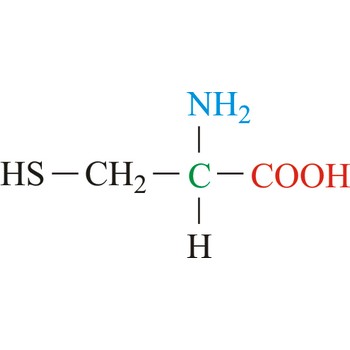
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
dipole moment → dipolni moment
Electric dipole moment (μ) is a product of the positive charge and the distance between the charges. Dipole moments are often stated in debyes; The SI unit is the coulomb metre. In a diatomic molecule, such as HCl, the dipole moment is a measure of the polar nature of the bond; i.e. the extent to which the average electron charges are displaced towards one atom (in the case of HCl, the electrons are attracted towards the more electronegative chlorine atom). In a polyatomic molecule, the dipole moment is the vector sum of the dipole moments of the individual bonds. In a symmetrical molecule, such as tetrafluoromethane (CF4) there is no overall dipole moment, although the individual C-F bonds are polar.
racemic mixture → racematna smjesa
Racemic mixture is a mixture of dextrorotatory and levorotatory optically active isomers in equal amounts. Because the two enantiomers rotate plane-polarised light in opposite directions, a racemic mixture does not rotate plane-polarised light. These mixtures are prefixed by ± or dl-.
dissociation → disocijacija
Dissociation is the process by which a chemical combination breaks up into simpler constituents as a result of either added energy (dissociated by heat), or the effect of a solvent on a dissolved polar compound (electrolytic dissociation). It may occur in the gaseous, solid, or liquid state, or in a solution.
An example of dissociation is the reversible reaction of hydrogen iodide at high temperatures
The term dissociation is also applied to ionisation reactions of acids and bases in water. For example
which is often regarded as a straightforward dissociation into ions
dropping mercury electrode → kapajuća živina elektroda
Dropping mercury electrode (DME) is a working electrode arrangement for polarography in which mercury continuously drops from a reservoir through a capillary tube (internal diameter 0.03 - 0.05 mm) into the solution. The optimum interval between drops for most analyses is between 2 and 5 s. The unique advantage to the use of the DME is that the constant renewal of the electrode surface, exposed to the test solution, eliminates the effects of electrode poisoning.
electronegativity → elektronegativnost
Electronegativity is a parameter originally introduced by L. Pauling which describes, on a relative basis, the power of an atom to attract electrons. For example, in hydrogen chloride, the chlorine atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen and the molecule is polar, with a negative charge on the chlorine atom.
There are various ways of assigning values for the electronegativity of an element. Pauling electronegativities are based on bond dissociation energies using a scale in which fluorine, the most electronegative element, has the value 4 and francium, the lowest electronegative element, has the value 0.7.
enantiomer → enantiomer
Enantiomers are a chiral molecule and its non-superposable mirror image. The two forms rotate the plane of polarised light by equal amounts in the opposite directions. Also called optical isomers.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Polar coordinates." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table