terbium → terbij
Terbium was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1843. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is soft, ductile, silvery-grey, rare earth metal. Oxidizes slowly in air. Reacts with cold water. Terbium is found with other rare earths in monazite sand. Other sources are xenotime and euxenite, both of which are oxide mixtures that can contain up to 1 % terbium. It is used in modest amounts in special lasers and solid-state devices.
thermal resistance → toplinski otpor
Heat always flows from a higher to a lower temperature level. The driving force for the heat flux lies in the temperature difference ΔT between two temperature levels. Analogous to Ohm’s law, the following holds:
where H = dQ/dt is heat flux, measured in watts, ΔT is temperature difference across the thermal resistance, measured in kelvin, and Rth is thermal resistance, measured in K/W.
For example, suppose there were two houses with walls of equal thickness; one is made of glass and the other of asbestos. On a cold day, heat would pass through the glass house much faster. The thermal restistance of asbestos is then higher than of glass.
If the thermal Ohm’s law is divided by the heat capacity C, Newton’s law of cooling is obtained:
where dT/dt is rate of cooling or heating, measured in K s-1, and C is heat capacity, measured in J K-1.
thorium → torij
Thorium was discovered by Jöns Jakob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1828. Named after Thor, the mythological Scandinavian god of war. It is heavy, grey, soft, malleable, ductile, radioactive metal. Tarnishes in air; reacts with water. Reacts violently with oxidants. Thorium is found in various minerals like monazite and thorite. Used in making strong alloys. Also in ultraviolet photoelectric cells. It is a common ingredient in high-quality lenses. Bombarded with neutrons make uranium-233, a nuclear fuel.
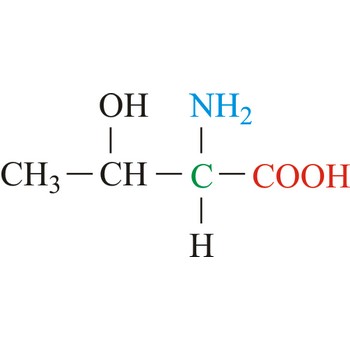
threonine → treonin
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
thulium → tulij
Thulium was discovered by Per Theodore Cleve (Sweden) in 1879. Named after Thule, an ancient name for Scandinavia. It is soft, malleable, ductile, silvery metal. Tarnishes in air. Reacts with water. Flammable dust. Thulium is found with other rare earths in the minerals gadolinite, euxenite, xenotime and monazite. Radioactive thulium is used to power portable X-ray machines, eliminating the need for electrical equipment.
titanium → titanij
Titanium was discovered by William Gregor (England) in 1791. Named after the Titans, the sons of the Earth goddess in Greek mythology. It is shiny, dark-grey metal. Powdered form burns in air. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. It can be highly polished and is relatively immune to tarnishing. Unreactive with alkali and most acids. Titanium usually occurs in the minerals ilmenite (FeTiO3), rutile (TiO2) and iron ores. Pure metal produced by heating TiO2 with C and Cl2 to produce TiCl4 then heated with Mg gas in Ar atmosphere. Since it is strong and resists acids it is used in many alloys. Titanium dioxide (TiO2), a white pigment that covers surfaces very well, is used in paint, rubber, paper and many others.
titar → titar
Titar (T) is a mass of titrated matter which is equivalent to 1 cm3 of solution. It is shown as T = 2.356 mg HCl / 1.0 cm3 NaOH, 0.1000 moldm-3, and it is usually shown in a table form. If the concentration of used standard solution (c) differs from one outlined in the table data (c0), the factor of correction (f) is induced
Titar is usually used in industrial operational laboratories where from titar tables mass or percentage of the ingredient in question is directly read.
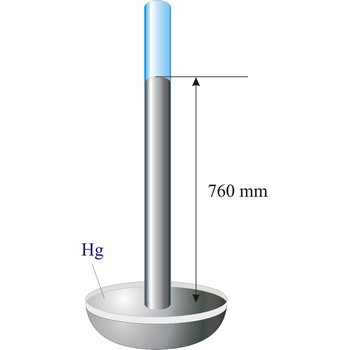
Torricelli, Evangelista → Torricelli, Evangelista
Evangelista Torricelli (1852-1908) is Italian physicist and mathematician. He became the first scientist to create a sustained vacuum and to discover the principle of a barometer. He filled a tube three feet long, and hermetically closed at one end, with mercury and set it vertically with the open end in a basin of mercury, taking care that no air-bubbles should get into the tube. The column of mercury invariably fell to about twenty-eight inches, leaving an empty space above its level. He discovered that the variation of the height of the mercury from day to day was caused by changes in the atmospheric pressure. He also constructed a number of large objectives and small, short focus, simple microscopes.
toxin → toksin
Toxins are effective and specific poisons produced by living organisms. They usually consist of an amino acid chain which can vary in molecular weight between a couple of hundred (peptides) and one hundred thousand (proteins). They may also be low-molecular organic compounds. Toxins are produced by numerous organisms, e.g., bacteria, fungi, algae and plants. Many of them are extremely poisonous, with a toxicity that is several orders of magnitude greater than the nerve agents. Botulinum toxin, produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, is the most poisonous substance known.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "PloÅ¡no centrirana kubiÄna reÅ¡etka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table