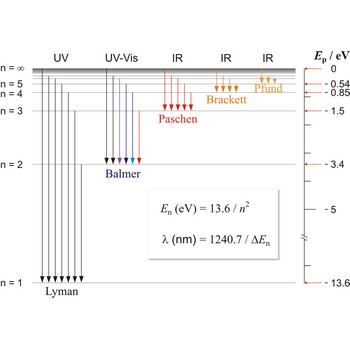
Paschen series → Paschenova serija
Paschen series are the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the state with principal quantum number n = 3 and successive higher states.
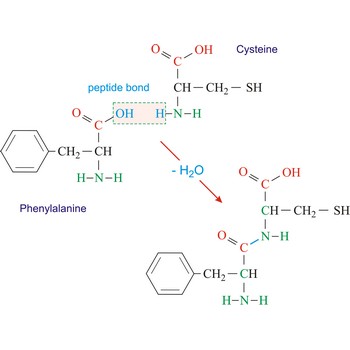
peptide bond → peptidna veza
Peptide bond emerges when two amino acid join in a way that the carbon atom from one connects with the nitrogen atom from the other (creating a C-N bond).
period → perioda
Periods are horizontal rows in the periodic table, each period begin with an alkali metal (one electron in the outermost principal quantum level) and ending with a noble gas (each having eight electrons in the outermost principal quantum level, except for helium, which is limited to two).
periodic table of the elements → periodni sustav elemenata
Periodic table is a table of elements, written in sequence in the order of atomic number or atomic weight and arranged in horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups) to illustrate the occurrence of similarities in the properties of the elements as a periodic function of the sequence. The original form was proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, using relative atomic masses.
Petri dish → Petrijeva zdjelica
Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic flat bottomed dish with a lid. Used primarily in laboratories for the culture of bacteria and other microorganisms on specially prepared media. It was named after the German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri (1852-1921) who invented it in 1877.
pH → pH
pH is a convenient measure of the acid-base character of a solution, usually defined by
where c(H+) is the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per litre. The more precise definition is in terms of activity rather than concentration.
A solution of pH 0 to 7 is acid, pH of 7 is neutral, pH over 7 to 14 is alkaline.
pickling → dekapiranje
Pickling is a process to chemically remove scale or oxide from steel to obtain a clean surface. When applied to bars or coils prior to bright drawing, the steel is immersed in a bath of dilute sulphuric acid (w(H2SO4) = 10 %) heated to a temperature of around 80 °C. An inhibitor is added to prevent attack and pitting of the cleaned metal. After pickling, a washing process takes place followed by immersion in a lime-water bath to neutralise any remaining acid.
piezoelectric effect → piezoelektrični efekt
Piezoelectric effect is voltage produced between surfaces of a solid dielectric (nonconducting substance) when a mechanical stress is applied to it. A small current may be produced as well. The effect, discovered by the French physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906) in 1883, is exhibited by certain crystals, e.g., quartz and Rochelle salt, and ceramic materials. When a voltage is applied across certain surfaces of a solid that exhibits the piezoelectric effect, the solid undergoes a mechanical distortion. Piezoelectric materials are used in transducers, e.g., phonograph cartridges, microphones, and strain gauges, which produce an electrical output from a mechanical input, and in earphones and ultrasonic radiators, which produce a mechanical output from an electrical input.
plasma → plazma
Plasma is a highly ionised gas in which the charge of the electrons is balanced by the charge of the positive ions, so that the system as a whole is electrically neutral. Plasmas are created by exposing gases at low pressure to an electric or electromagnetic field. In semiconductor processing, plasmas are used for etching and thin film deposition (the excited state of the gas makes it very reactive). In everyday life plasmas are used to give light in fluorescent light bulbs, neon lamps, and blue insect traps.
pipette → pipeta
Pipettes are glass tubes which are tapers towards at both ends into narrow opened tubes. According to their design two types of pipettes can be distinguished:
Volumetric pipettes
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette
Graduated pipettes
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. They are filled in the same way as volumetric ones and liquid can be gradually released.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "PloÅ¡no centrirana kubiÄna reÅ¡etka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table