Carnot cycle → Carnotov kružni proces
Carnot cycle is the most efficient cycle of operations for a reversible heat engine. Published in 1824 by French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), it consists of four operations on the working substance in the engine:
1-2: Isothermal expansion at thermodynamic temperature T1 with heat QH taken in.
2-3: Adiabatic expansion with a fall of temperature to T2.
3-4: Isothermal compression at temperature T2 with heat QC given out.
4-1: Adiabatic compression at temperature back to T1.
According to the Carnot principle, the efficiency of any reversible heat engine depends only on the temperature range through which it works, rather than the properties of the working substances.
cathode → katoda
Cathode is a negative electrode of an electrolytic cell to which positively charged ions (cations) migrate when a current is passed as in electroplating baths.
In a primary or secondary cell (battery or accumulator) the cathode is the electrode that spontaneously becomes negative during discharge, and form which therefore electrons emerge.
In vacuum electronic devices electrons are emitted by the cathode and flow to the anode.
electron volt → elektronvolt
Electron volt (eV) is a non-SI unit of energy used in atomic and nuclear physics, equal to approximately 1.602 177×10-19 J. The electron volt is defined as the kinetic energy acquired by an electron upon acceleration through a potential difference of 1 V.
elementary particle → elementarna čestica
Elementary particle is one of fundamental particles of which matter is composed, such as the electron, proton or neutron.
environment protection → zaštita okoliša
From Environment protection law of the Republic of Croatia: By protection of the environment, the following is ensured: complete preservation of environment quality, natural community preservation, rational usage of natural resources and energy in the most favourable way concerning the environment as a basic condition of healthy and sustainable development.
equivalent weight → ekvivalentna masa
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in a neutralization reaction is that mass of substance (molecule, ion, or paired ion) that either reacts with or supplies 1 mol of hydrogen ions in that reaction.
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in an oxidation/reduction reaction is that weight which directly or indirectly produces or consumes 1 mol of electrons.
cathode ray → katodna zraka
Cathode ray is a negatively charged beam that emanates from the cathode of a discharge tube. Cathode rays are streams of electrons.
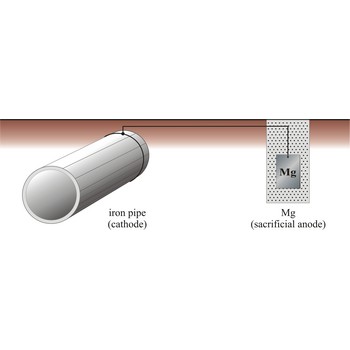
cathodic protection → katodna zaštita
Cathodic protection is a process in which a structural metal, such as iron, is protected from corrosion by connecting it to a metal that has a more negative reduction half-cell potential, which now corrodes instead of iron. There are two major variations of the cathodic method of corrosion protection. The first is called the impressed current method, and the other is called the sacrificial anode method.
cellulose → celuloza
Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n, is a polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by (1→4)-β-glycoside bonds. Nature uses cellulose primarily as a structural material to impart strength and rigidity to plants. Leaves, grasses, and cotton are primarily cellulose. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc. Cellulose also serves as raw material for the manufacture of cellulose acetate, known commercially as acetate rayon, and cellulose nitrate, known as guncotton. Gunncotton is the major ingredient in smokeless powder, the explosive propellant used in artillery shells and in ammunition for firearms.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "PloÅ¡no centrirana kubiÄna reÅ¡etka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table