chemical equation equalization → izjednačavanje kemijske jednadžbe
Chemical equation equalization is determining values of stechiometric coefficients of reactants and products in a chemical equation in a way that the number of atoms of each element is equal before and after the reaction.
chlorination → kloriranje
1. Chlorination is an addition or substitution of chlorine in organic compounds.
2. Chlorination is a sterilisation of drinking and swimming pool water or oxidation of undesirable impurities, using chlorine or its compounds.
coal → ugljen
Coal is a black or brownish-black, combustible sedimentary rock, with 30 % (lignite) to 98 % (anthracite) carbon by weight, mixed with various amounts of water and small amounts of sulfur and nitrogen compounds. It is formed from plant matter that decayed in swamps and bogs that has been compressed and altered by geological processes over millions of years. Coal is primarily used as a fuel.
coal tar → ugljeni katran
Coal tar is a material obtained from the destructive distillation of coal in the production of coal gas. The crude tar contains a large number of organic compounds (e.g. benzene, naphthalene, methylbenzene, etc.), which can be separated by fractional distillation.
beta particle → beta-čestica
Beta particle is a charged particle emitted from a radioactive atomic nucleus either natural or manufactured. The energies of beta particles range from 0 MeV to 4 MeV. They carry a single charge; if this is negative, the particle is identical with an electron; if positive, it is a positron.
An unstable atomic nucleus changes into a nucleus of the same mass number but different proton number with the emission of an electron and an antineutrino (or a positron and a neutrino)
beta-glucan → beta-glukan
Beta-glucans are are naturally occurring polysaccharides that contain only glucose as structural components, and are linked with β-glycosidic bonds. They is the most known powerful immune stimulant. The most active forms of β-glucans are those comprising D-glucose units with β(1→3) links and with short side-chains of D-glucose attached at the β(1→6) position. These are referred to as beta-1,3/1,6 glucan. They are a major component of soluble dietary fiber, which can be found in cereal grains (oats, barley, wheat), yeast, and certain mushrooms (shiitake, maitake).
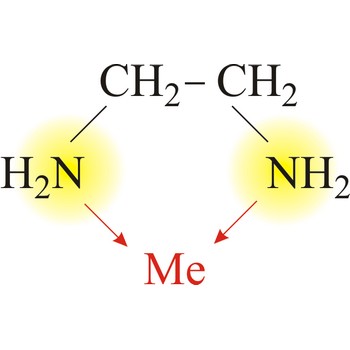
bidentate ligand → bidentatni ligand
Bidentate ligand is a ligand that has two "teeth" or atoms that coordinate directly to the central atom in a complex. An example of a bidentate ligand is ethylenediamine. A single molecule of ethylenediamine can form two bonds to a metal ion. The bonds form between the metal ion and the nitrogen atoms of ethylenediamine.
bismuth → bizmut
Bismuth was discovered by Claude Geoffroy (France) in 1753. The origin of the name comes from the German words Weisse Masse meaning white mass; now spelled wismut and bisemutum. It is hard, brittle, steel-grey metal with a pink tint. Stable in oxygen and water. Dissolves in concentrated nitric acid. Bismuth can be found free in nature and in minerals like bismuthine (Bi2S3) and in bismuth ochre (Bi2O3) Main use is in pharmaceuticals and low melting point alloys used as fuses.
colligative properties → koligativna svojstva
Colligative properties are properties which affect a solvent based on the number of molecules of solute present such as melting point, boiling point and osmotic pressure.
computational chemistry → kompjutacijska kemija
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry concerned with the prediction or simulation of chemical properties, structures, or processes using numerical techniques.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "PloÅ¡no centrirana kubiÄna reÅ¡etka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table