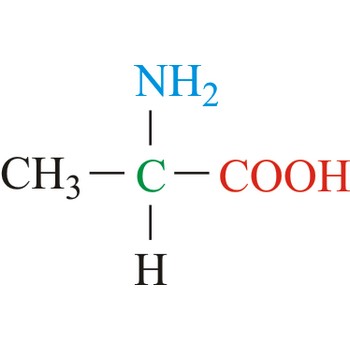
alanine → alanin
Alanine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is the second simplest amino acid, but used the most in proteins. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Alanine is a nonessential amino acid, meaning it can be manufactured by the human body, and does not need to be obtained directly through the diet.
- Abbreviations: Ala, A
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2
- Molecular weight: 89.09 g/mol
average rate of reaction → prosječna brzina reakcije
Average rate of reaction is calculated in a way that a total change of reactants and products concentration is divided with time which is needed for reaction to end.
alkanes → alkani
Alkanes (paraffins) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n+2, and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkane names end in the suffix -ane. They form a homologous series (the alkane series) methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), etc. The lower members of the series are gases; the high-molecular mass alkanes are waxy solid. Generaly the alkanes are fairly unreactive. They form haloalkanes with halogens when irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. Alkanes are present in natural gas and petroleum.
alkenes → alkeni
Alkenes are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having one or more double carbon-carbon bonds in their molecules. In the systematic chemical nomenclature, alkene names end in the suffix -ene. The general formula is CnH(2n+2)-2x were x is the number of double bonds. Alkenes that have only one double bond form a homologous series: ethene (ethylene), CH2=CH2, propene, CH3CH2=CH2, etc. Alkenes typically undergo addition reactions to the double bond.
alkynes → alkini
Alkynes (acetylenes) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having one or more triple carbon-carbon bond. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkyne names end in the suffix -yne. The general formula is CnH(2n+2)-4x were x is the number of triple bonds. Alkynes that have only one triple bond form a homologous series: ethyne (acetylene), CH≡CH, propyne, CH3CH≡CH, etc. Like alkenes, alkynes undergo addition reaction.
Allihn condenser → Allihnovo hladilo
Allihn condenser or bulb condenser consists of an outer water jacket and the inner glass tube with a series of spherical bubbles to maximize the thermal contact with the cooling water. It is named after its inventor, the German chemist Felix Richard Allihn (1854-1915).
Avogadro constant → Avogadrova konstanta
Avogadro constant (NA or L) is the number of elementary entities in one mole of a substance.
It has the value (6.022 045±0.000 031)×1023 mol-1.
Avogadro’s law → Avogadrov zakon
Avogadro’s law: Equal volumes of all gases contain equal numbers of molecules at the same pressure and temperature. The law, often called Avogadro’s hypothesis, is true only for ideal gases. It was proposed in 1811 by Italian chemist Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856).
becquerel → bekerel
Becquerel (Bq) is the SI derived unit, with a special name, for radioactivity, equal to s-1. It describes a radioactivity of an amount of radionuclide decaying at the rate, on average, of one spontaneous nuclear transition per second. The unit was named after the French scientist Antoine Henri Becquerel (1852-1908) (disintegrations per unit time), equal to s-1.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "PloÅ¡no centrirana kubiÄna reÅ¡etka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table