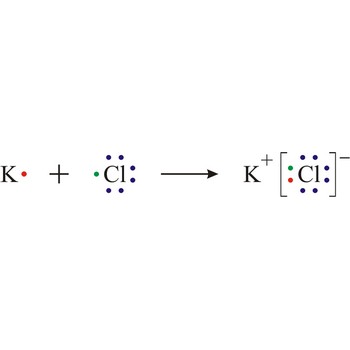upper flammable limit → gornja granica zapaljivosti
Upper flammable limit (UEL) or the upper explosive limit is the maximum concentration of vapour or gas in air below which propagation of flame does not occur on contact with a source of ignition. The mixture is said to be too rich.
ionic bond → ionska veza
Ionic bond is a strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. Typically chemical bonds have energies of about 100 kJ mol-1. Ionic bond is a bond at which one of the participants, during the procedure of bonding, gives away its unpaired electrons to another atom so that both can achieve electron arrangement of the closest noble gas. In order to form an ionic bond one of the atoms must cross to the positively charged ion by losing certain number of electrons and the other atom must receive those electrons and cross to the negatively charged ion.
Joule-Thomson coefficient → Joule-Thompsonov koeficijent
Joule-Thomson coefficient (μ) is a parameter which describes the temperature change when a gas expands adiabatically through a nozzle from a high pressure to a low pressure region. It is defined by
where H is enthalpy.
Joule-Thomson’s effect → Joule-Thomsonov efekt
Temperature of ideal gas will not be changed when it is repressed to a lower pressure, but when real gases are repressed to a lower pressure, a lower or higher temperature change appears under high pressures. The temperature change which appears at real gas expansion in a system into which energy is not brought is called Joule-Thomson’s effect. It was determined that when air is repressed by 1 bar, its temperature drops by 0.25 °C. That minute effect is completely irrelevant for most technical processes, but is also used in gas liquefying procedure.
vapour pressure → tlak pare
Vapour pressure is the pressure of a gas in equilibrium with a liquid (or, in some usage, a solid) at a specified temperature.
vertical ionisation energy → vertikalna energija ionizacije
Vertical ionisation energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, molecule, or ion in the gas phase without moving any nuclei. The vertical ionisation energy is greater than or equal to the adiabatic ionisation energy.
kinetic energy → kinetička energija
Kinetic energy (Ek) is associated with the state of motion of a body. It is a scalar property and defined to be
Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
krypton → kripton
Krypton was discovered by Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers (England) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word kryptos meaning hidden. It is colourless, odourless rare noble gas. Reacts only with fluorine. Krypton is obtained from production of liquid air. Used in lighting products. Some is used as inert filler-gas in incandescent bulbs. Some is mixed with argon in fluorescent lamps. The most important use is in flashing stroboscopic lamps that outline airport runways.
law of conservation of mass → zakon o očuvanju mase
Law of conservation of mass states that no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. The state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction, for example, from a solid to a gas, but its total mass will not change. Note that the energy released (exothermic) or adsorbed (endothermic) in a chemical reaction is a result of energy transfer between atoms and their environment.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Plin nositelj." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table