fire-damp → plin praskavac
Fire-damp is a mixture of two volume parts of hydrogen and one volume part of oxygen which, if set on fire, strongly explodes, the flame giving of a very high temperature (2 000 °C).
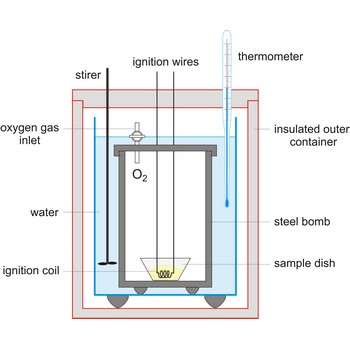
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
boron → bor
Boron compounds have been known for thousands of years, but the element was not discovered until 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy (England) and independently by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac (France) and L. J. Thenard (France). The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word buraq and the Persian word burah meaning boraks. It is hard, brittle, lustrous black semimetal. Unreactive with oxygen, water, alkalis or acids. Combines with most metals to form borides. Boron is obtained from kernite, a kind of borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O). High purity boron is produced by electrolysis of molten potassium fluroborate and potassium chloride (KCl). Amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares to provide a distinctive green color and in rockets as an igniter.
caesium → cezij
Caesium was discovered by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (Germany) in 1860. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word caesius meaning sky blue or heavenly blue. It is very soft, light grey, ductile metal. Reacts readily with oxygen. Reacts explosively with water. Caesium is found in pollucite [(Cs4Al4Si9O26)·H2O] and as trace in lepidolite. Used as a ’getter’ to remove air traces in vacuum and cathode-ray tubes. Also used in producing photoelectric devices and atomic clocks. Since it ionises readily, it is used as an ion rocket motor propellant.
luminescent flame → svijetleći plamen
Luminescent flame is produced when there is not enough oxygen for complete burnout.
neptunium → neptunij
Neptunium was discovered by Edwin M. McMillan and P. H. Abelson (USA) in 1940. Named after the planet Neptune. It is rare, silvery radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; reacts with oxygen and acids. Attacked by steam. Radiotoxic. Neptunium was produced by bombarding uranium with slow neutrons.
oxidation → oksidacija
The term oxidation originally meant a reaction in which oxygen combines chemically with another substance. More generally, oxidation is a part of a chemical reaction in which a reactant loses electrons (increases oxidation number). Simultaneous reduction of a different reactant must occur (redox reaction).
polyvalent element → polivalentni elementi
Polyvalent element is a molecule which having more than one valence, for example oxygen is a divalent in H2O, nitrogen is a trivalent in NH3, carbon is a tetravalent in methane (CH4).
calcium → kalcij
Calcium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word calix meaning lime. It is fairly hard, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces form oxides and nitrides. Reacts with water and oxygen. Occurs only in compounds. Calcium is obtained from minerals like chalk, limestone and marble. Pure metal is produced by replacing the calcium in lime (CaCO3) with aluminium in hot, low pressure retorts. Used by many forms of life to make shells and bones. Virtually no use for the pure metal, however two of its compounds are, lime (CaO) and gypsum (CaSO4), are in great demand by a number of industries.
carbon → ugljik
Carbon has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word carbo meaning charcoal. Graphite form of carbon is a black, odourless, slippery solid. Graphite sublimes at 3825 °C. Diamond form is a clear or colored; an extremely hard solid. C60 is Buckminsterfullerine. Carbon black burns readily with oxidants. Carbon is made by burning organic compounds with insufficient oxygen. There are close to ten million known carbon compounds, many thousands of which are vital to organic and life processes. Radiocarbon dating uses the carbon-14 isotope to date old objects.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Oxygen meter for oxygen concentrator." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table