aliphatic compound → alifatski spoj
Aliphatic compounds are acyclic or cyclic, saturated or unsaturated carbon compounds, excluding aromatic compounds.
chemical compound → kemijski spoj
Some substance is a compound only if it can be decomposed into two or more different substances by means of a chemical reaction. If two or more substances react, thus creating a new substance, that new substance is called a chemical compound.
covalent compound → kovalentni spoj
Covalent compound is a compound made of molecules - not ions, such as H2O, CH4, Cl2. The atoms in the compound are bound together by shared electrons. Also called a molecular compound.
chemical compound formula → formula kemijskog spoja
Chemical elements are represented by their symbols, and chemical compounds are represented by a group of symbols of those elements from which the compound is composed. That group of symbols, which shows which atoms and in which number relation they are present in certain compound is called a chemical compound formula.
In a formula chemical symbols show which element is present in a certain compound, and its index shows how much of that element there is in a certain compound. From sulphuric acid formula H2SO4 we can see that one molecule of sulphuric acid consists of two atoms of hydrogen, one atom of sulphur and four atoms of oxygen.
cyclic compound → ciklički spoj
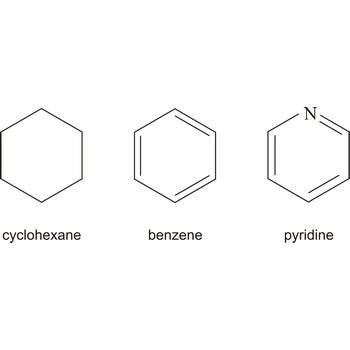
Cyclic describing a compound that has a ring of atoms in its molecules. In homocyclic compounds all the atoms in the ring are of the same type, e.g. benzene (C6H6) and cyclohexane (C6H12). These two examples are also examples of carbocyclic compounds; i.e. the rings are made of carbon atoms. If different atoms occur in the ring, as in pyridine (C5H5N), the compound is said to be heterocyclic.
nitroso compound → nitrozo spoj
Nitroso compounds are compounds that contain the nitroso-group (.NO).
organometallic compound → organometalni spoj
Organometallic compounds are compounds in which there is a covalent connection between atoms of carbons and atoms of metal (C-Me).
oxo compound → okso-spoj
Oxo compounds are organic compounds that contain the karbonyl group, C=O. The term thus embraces aldehydes, carboxylic acids, ketones, amides, and esters.
aromatic compounds → aromatski ugljikovodici
Aromatic compounds are a major group of unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons containing one or more rings, typified by benzene, which has a 6-carbon ring containing three double bonds. All the bonds in benzene (C6H6) are the same length intermediate between double and single C-C bonds. The properties arise because the electrons in the p-orbitals are delocalised over the ring, giving extra stabilization energy of 150 kJ/mol over the energy of Kekulé structure. Aromatic compounds are unsaturated compounds, yet they do not easily partake in addition reactions.
Historical use of the term implies a ring containing only carbon (e.g., benzene, naphthalene), but it is often generalized to include heterocyclic structures such as pyridine and thiophene.
azo compounds → azo-spojevi
Azo compounds are organic compounds containing the group -N=N- linking two other groups. They can be formed by reaction of a diazonium ion with a benzene ring.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Oxo compound." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table