vapour pressure lowering → snižavanje tlaka pare
Vapour pressure is a colligative property of solutions. The vapour pressure of a solution is always lower than the vapour pressure of the pure solvent. Ratio of solution to pure solvent vapour pressures is approximately equal to the mole fraction of solvent in the solution.
white spirit → bijeli špirit
White spirit (mineral spirits, petroleum spirits) is a paraffin-derived clear, transparent liquid which is a common organic solvent used in painting and decorating.
supercritical fluid extraction → superkritična fluidna ekstrakcija
Supercritical fluid extractions (SFE) have solvating powers similar to liquid organic solvents, but with higher diffusivities, lower viscosity, and lower surface tension. The main advantages of using supercritical fluids for extractions is that they are inexpensive, contaminant free, and less costly to dispose safely than organic solvents. For non-destructive isolation choose SFE, which is simply the best technology for sensitive raw materials. For these reasons supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is the reagent used to extract caffeine from coffee and tea. Its gaslike behavior allows it to penetrate deep into the green coffee beans, and it dissolves from 97 % to 99 % of the caffeine present.
thin layer chromatography → tankoslojna kromatografija
Thin layer chromatography. (TLC) is a technique for separating components in a mixture on the basis of their differing polarities. A spot of sample is placed on a flat sheet coated with silica and then carried along by a solvent that soaks the sheet. Different components will move different distances over the surface. TLC is a useful screening technique in clinical chemistry; for example, it can be used to detect the presence of drugs in urine.
water → voda
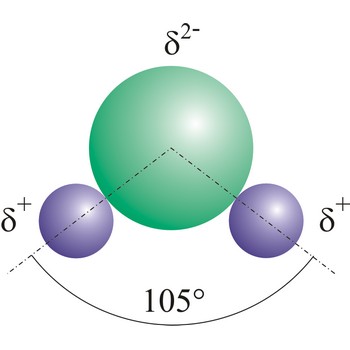
Water (H2O) (dihydrogen oxide) is a binary compound that occurs at room temperature as a clear colorless odorless tasteless liquid; freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C. Water is a chemical compound which is essential for living organisms and it is widely used as a solvent.
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Otapalo." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table